7.2 Binary tree traversal¶
From the perspective of physical structure, a tree is a data structure based on linked lists, hence its traversal method involves accessing nodes one by one through pointers. However, a tree is a non-linear data structure, which makes traversing a tree more complex than traversing a linked list, requiring the assistance of search algorithms to achieve.
Common traversal methods for binary trees include level-order traversal, preorder traversal, inorder traversal, and postorder traversal, among others.
7.2.1 Level-order traversal¶
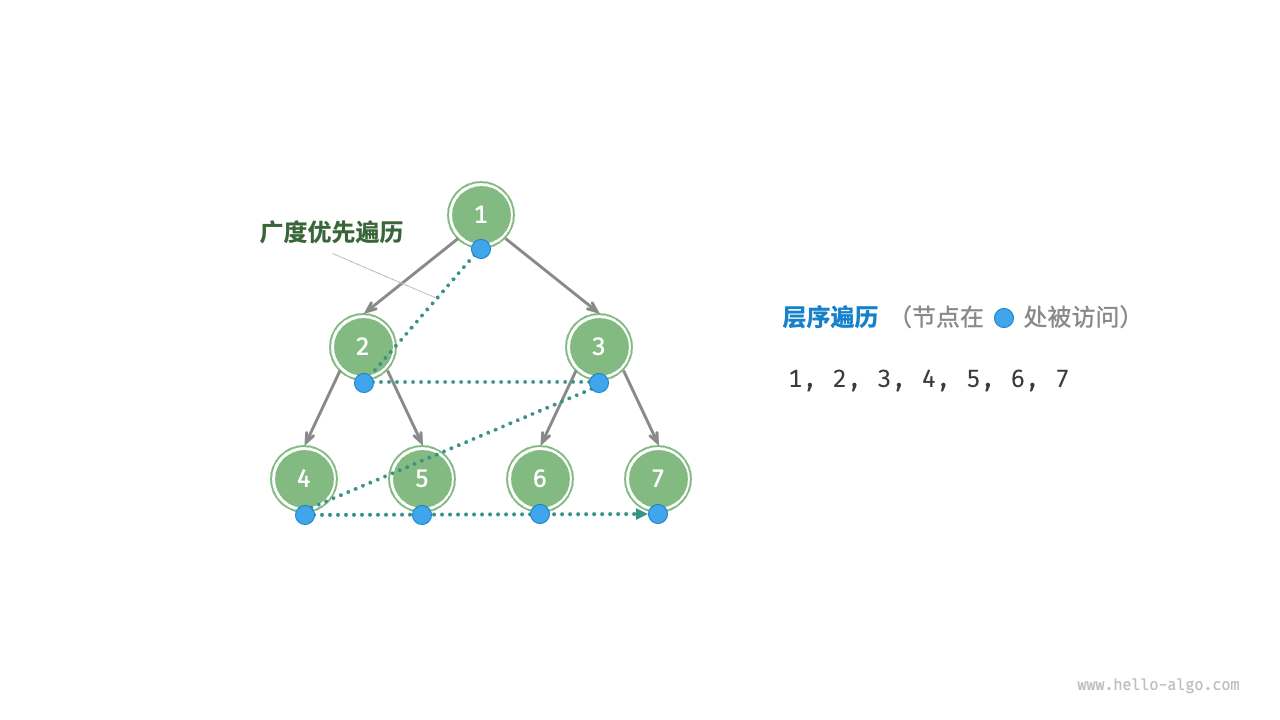
As shown in the Figure 7-9 , "level-order traversal" traverses the binary tree from top to bottom, layer by layer, and accesses nodes in each layer in a left-to-right order.
Level-order traversal essentially belongs to "breadth-first traversal", also known as "breadth-first search (BFS)", which embodies a "circumferentially outward expanding" layer-by-layer traversal method.
Figure 7-9 Level-order traversal of a binary tree
1. Code implementation¶
Breadth-first traversal is usually implemented with the help of a "queue". The queue follows the "first in, first out" rule, while breadth-first traversal follows the "layer-by-layer progression" rule, the underlying ideas of the two are consistent. The implementation code is as follows:
def level_order(root: TreeNode | None) -> list[int]:
"""层序遍历"""
# 初始化队列,加入根节点
queue: deque[TreeNode] = deque()
queue.append(root)
# 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
res = []
while queue:
node: TreeNode = queue.popleft() # 队列出队
res.append(node.val) # 保存节点值
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left) # 左子节点入队
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right) # 右子节点入队
return res
/* 层序遍历 */
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode *root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
queue<TreeNode *> queue;
queue.push(root);
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
vector<int> vec;
while (!queue.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = queue.front();
queue.pop(); // 队列出队
vec.push_back(node->val); // 保存节点值
if (node->left != nullptr)
queue.push(node->left); // 左子节点入队
if (node->right != nullptr)
queue.push(node->right); // 右子节点入队
}
return vec;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
List<Integer> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll(); // 队列出队
list.add(node.val); // 保存节点值
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left); // 左子节点入队
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right); // 右子节点入队
}
return list;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
List<int> LevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new();
queue.Enqueue(root);
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
List<int> list = [];
while (queue.Count != 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.Dequeue(); // 队列出队
list.Add(node.val!.Value); // 保存节点值
if (node.left != null)
queue.Enqueue(node.left); // 左子节点入队
if (node.right != null)
queue.Enqueue(node.right); // 右子节点入队
}
return list;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) []any {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
queue := list.New()
queue.PushBack(root)
// 初始化一个切片,用于保存遍历序列
nums := make([]any, 0)
for queue.Len() > 0 {
// 队列出队
node := queue.Remove(queue.Front()).(*TreeNode)
// 保存节点值
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
if node.Left != nil {
// 左子节点入队
queue.PushBack(node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
// 右子节点入队
queue.PushBack(node.Right)
}
}
return nums
}
/* 层序遍历 */
func levelOrder(root: TreeNode) -> [Int] {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
var queue: [TreeNode] = [root]
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
var list: [Int] = []
while !queue.isEmpty {
let node = queue.removeFirst() // 队列出队
list.append(node.val) // 保存节点值
if let left = node.left {
queue.append(left) // 左子节点入队
}
if let right = node.right {
queue.append(right) // 右子节点入队
}
}
return list
}
/* 层序遍历 */
function levelOrder(root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
const queue = [root];
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
const list = [];
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue.shift(); // 队列出队
list.push(node.val); // 保存节点值
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left); // 左子节点入队
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right); // 右子节点入队
}
return list;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
function levelOrder(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
const queue = [root];
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
const list: number[] = [];
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue.shift() as TreeNode; // 队列出队
list.push(node.val); // 保存节点值
if (node.left) {
queue.push(node.left); // 左子节点入队
}
if (node.right) {
queue.push(node.right); // 右子节点入队
}
}
return list;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
List<int> levelOrder(TreeNode? root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
Queue<TreeNode?> queue = Queue();
queue.add(root);
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
List<int> res = [];
while (queue.isNotEmpty) {
TreeNode? node = queue.removeFirst(); // 队列出队
res.add(node!.val); // 保存节点值
if (node.left != null) queue.add(node.left); // 左子节点入队
if (node.right != null) queue.add(node.right); // 右子节点入队
}
return res;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
fn level_order(root: &Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>) -> Vec<i32> {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
let mut que = VecDeque::new();
que.push_back(Rc::clone(&root));
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
let mut vec = Vec::new();
while let Some(node) = que.pop_front() {
// 队列出队
vec.push(node.borrow().val); // 保存节点值
if let Some(left) = node.borrow().left.as_ref() {
que.push_back(Rc::clone(left)); // 左子节点入队
}
if let Some(right) = node.borrow().right.as_ref() {
que.push_back(Rc::clone(right)); // 右子节点入队
};
}
vec
}
/* 层序遍历 */
int *levelOrder(TreeNode *root, int *size) {
/* 辅助队列 */
int front, rear;
int index, *arr;
TreeNode *node;
TreeNode **queue;
/* 辅助队列 */
queue = (TreeNode **)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode *) * MAX_SIZE);
// 队列指针
front = 0, rear = 0;
// 加入根节点
queue[rear++] = root;
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
/* 辅助数组 */
arr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_SIZE);
// 数组指针
index = 0;
while (front < rear) {
// 队列出队
node = queue[front++];
// 保存节点值
arr[index++] = node->val;
if (node->left != NULL) {
// 左子节点入队
queue[rear++] = node->left;
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
// 右子节点入队
queue[rear++] = node->right;
}
}
// 更新数组长度的值
*size = index;
arr = realloc(arr, sizeof(int) * (*size));
// 释放辅助数组空间
free(queue);
return arr;
}
/* 层序遍历 */
fun levelOrder(root: TreeNode?): MutableList<Int> {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode?>()
queue.add(root)
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
val list = ArrayList<Int>()
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
val node = queue.poll() // 队列出队
list.add(node?.value!!) // 保存节点值
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left) // 左子节点入队
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right) // 右子节点入队
}
return list
}
// 层序遍历
fn levelOrder(comptime T: type, mem_allocator: std.mem.Allocator, root: *inc.TreeNode(T)) !std.ArrayList(T) {
// 初始化队列,加入根节点
const L = std.TailQueue(*inc.TreeNode(T));
var queue = L{};
var root_node = try mem_allocator.create(L.Node);
root_node.data = root;
queue.append(root_node);
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
var list = std.ArrayList(T).init(std.heap.page_allocator);
while (queue.len > 0) {
var queue_node = queue.popFirst().?; // 队列出队
var node = queue_node.data;
try list.append(node.val); // 保存节点值
if (node.left != null) {
var tmp_node = try mem_allocator.create(L.Node);
tmp_node.data = node.left.?;
queue.append(tmp_node); // 左子节点入队
}
if (node.right != null) {
var tmp_node = try mem_allocator.create(L.Node);
tmp_node.data = node.right.?;
queue.append(tmp_node); // 右子节点入队
}
}
return list;
}
Code Visualization
2. Complexity analysis¶
- Time complexity is \(O(n)\): All nodes are visited once, using \(O(n)\) time, where \(n\) is the number of nodes.
- Space complexity is \(O(n)\): In the worst case, i.e., a full binary tree, before traversing to the lowest level, the queue can contain at most \((n + 1) / 2\) nodes at the same time, occupying \(O(n)\) space.
7.2.2 Preorder, inorder, and postorder traversal¶
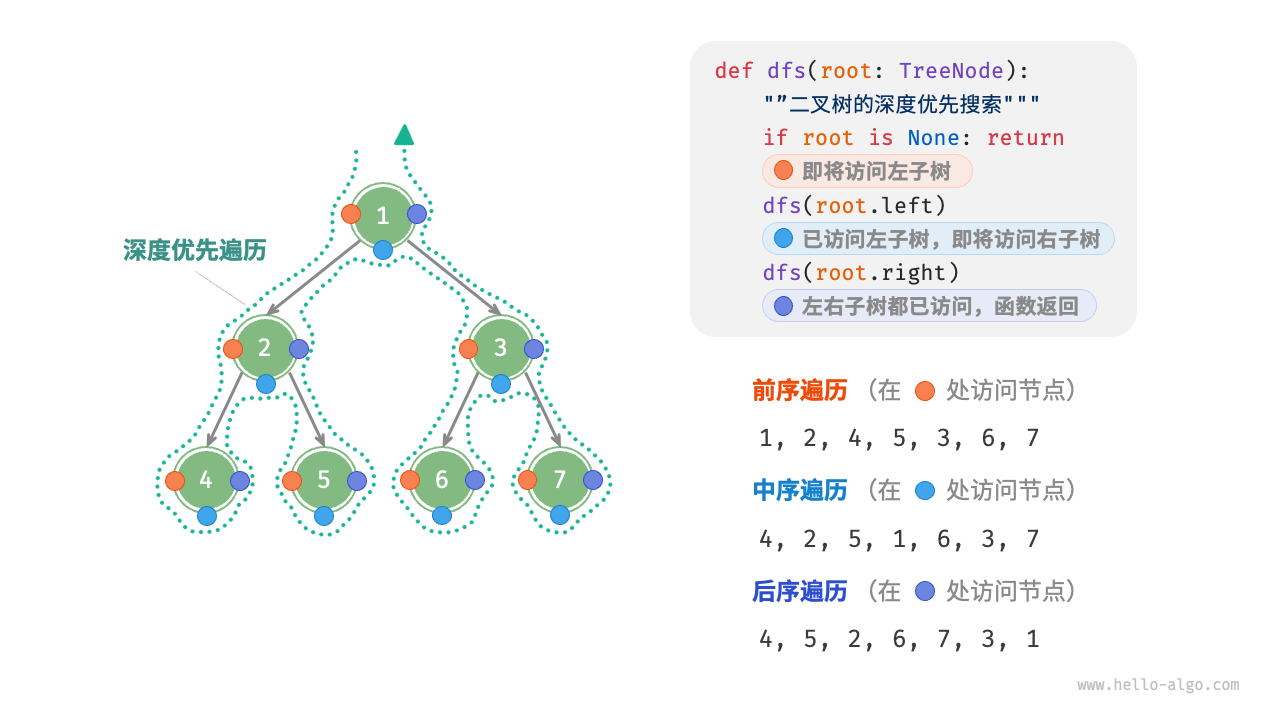
Correspondingly, preorder, inorder, and postorder traversal all belong to "depth-first traversal", also known as "depth-first search (DFS)", which embodies a "proceed to the end first, then backtrack and continue" traversal method.
The Figure 7-10 shows the working principle of performing a depth-first traversal on a binary tree. Depth-first traversal is like walking around the perimeter of the entire binary tree, encountering three positions at each node, corresponding to preorder traversal, inorder traversal, and postorder traversal.
Figure 7-10 Preorder, inorder, and postorder traversal of a binary search tree
1. Code implementation¶
Depth-first search is usually implemented based on recursion:
def pre_order(root: TreeNode | None):
"""前序遍历"""
if root is None:
return
# 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
res.append(root.val)
pre_order(root=root.left)
pre_order(root=root.right)
def in_order(root: TreeNode | None):
"""中序遍历"""
if root is None:
return
# 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
in_order(root=root.left)
res.append(root.val)
in_order(root=root.right)
def post_order(root: TreeNode | None):
"""后序遍历"""
if root is None:
return
# 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
post_order(root=root.left)
post_order(root=root.right)
res.append(root.val)
/* 前序遍历 */
void preOrder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
vec.push_back(root->val);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void inOrder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root->left);
vec.push_back(root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void postOrder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
vec.push_back(root->val);
}
/* 前序遍历 */
void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
list.add(root.val);
}
/* 前序遍历 */
void PreOrder(TreeNode? root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.Add(root.val!.Value);
PreOrder(root.left);
PreOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void InOrder(TreeNode? root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
InOrder(root.left);
list.Add(root.val!.Value);
InOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void PostOrder(TreeNode? root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
PostOrder(root.left);
PostOrder(root.right);
list.Add(root.val!.Value);
}
/* 前序遍历 */
func preOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
preOrder(node.Left)
preOrder(node.Right)
}
/* 中序遍历 */
func inOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(node.Left)
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
inOrder(node.Right)
}
/* 后序遍历 */
func postOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(node.Left)
postOrder(node.Right)
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
}
/* 前序遍历 */
func preOrder(root: TreeNode?) {
guard let root = root else {
return
}
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.append(root.val)
preOrder(root: root.left)
preOrder(root: root.right)
}
/* 中序遍历 */
func inOrder(root: TreeNode?) {
guard let root = root else {
return
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root: root.left)
list.append(root.val)
inOrder(root: root.right)
}
/* 后序遍历 */
func postOrder(root: TreeNode?) {
guard let root = root else {
return
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root: root.left)
postOrder(root: root.right)
list.append(root.val)
}
/* 前序遍历 */
function preOrder(root) {
if (root === null) return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.push(root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
function inOrder(root) {
if (root === null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left);
list.push(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
function postOrder(root) {
if (root === null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
list.push(root.val);
}
/* 前序遍历 */
function preOrder(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.push(root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
function inOrder(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left);
list.push(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
function postOrder(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
list.push(root.val);
}
/* 前序遍历 */
void preOrder(TreeNode? node) {
if (node == null) return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.add(node.val);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void inOrder(TreeNode? node) {
if (node == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(node.left);
list.add(node.val);
inOrder(node.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void postOrder(TreeNode? node) {
if (node == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
list.add(node.val);
}
/* 前序遍历 */
fn pre_order(root: Option<&Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut result = vec![];
if let Some(node) = root {
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
result.push(node.borrow().val);
result.append(&mut pre_order(node.borrow().left.as_ref()));
result.append(&mut pre_order(node.borrow().right.as_ref()));
}
result
}
/* 中序遍历 */
fn in_order(root: Option<&Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut result = vec![];
if let Some(node) = root {
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
result.append(&mut in_order(node.borrow().left.as_ref()));
result.push(node.borrow().val);
result.append(&mut in_order(node.borrow().right.as_ref()));
}
result
}
/* 后序遍历 */
fn post_order(root: Option<&Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut result = vec![];
if let Some(node) = root {
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
result.append(&mut post_order(node.borrow().left.as_ref()));
result.append(&mut post_order(node.borrow().right.as_ref()));
result.push(node.borrow().val);
}
result
}
/* 前序遍历 */
void preOrder(TreeNode *root, int *size) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
arr[(*size)++] = root->val;
preOrder(root->left, size);
preOrder(root->right, size);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void inOrder(TreeNode *root, int *size) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root->left, size);
arr[(*size)++] = root->val;
inOrder(root->right, size);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void postOrder(TreeNode *root, int *size) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root->left, size);
postOrder(root->right, size);
arr[(*size)++] = root->val;
}
/* 前序遍历 */
fun preOrder(root: TreeNode?) {
if (root == null) return
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.add(root.value)
preOrder(root.left)
preOrder(root.right)
}
/* 中序遍历 */
fun inOrder(root: TreeNode?) {
if (root == null) return
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left)
list.add(root.value)
inOrder(root.right)
}
/* 后序遍历 */
fun postOrder(root: TreeNode?) {
if (root == null) return
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
postOrder(root.left)
postOrder(root.right)
list.add(root.value)
}
// 前序遍历
fn preOrder(comptime T: type, root: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) !void {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
try list.append(root.?.val);
try preOrder(T, root.?.left);
try preOrder(T, root.?.right);
}
// 中序遍历
fn inOrder(comptime T: type, root: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) !void {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
try inOrder(T, root.?.left);
try list.append(root.?.val);
try inOrder(T, root.?.right);
}
// 后序遍历
fn postOrder(comptime T: type, root: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) !void {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
try postOrder(T, root.?.left);
try postOrder(T, root.?.right);
try list.append(root.?.val);
}
Code Visualization
Tip
Depth-first search can also be implemented based on iteration, interested readers can study this on their own.
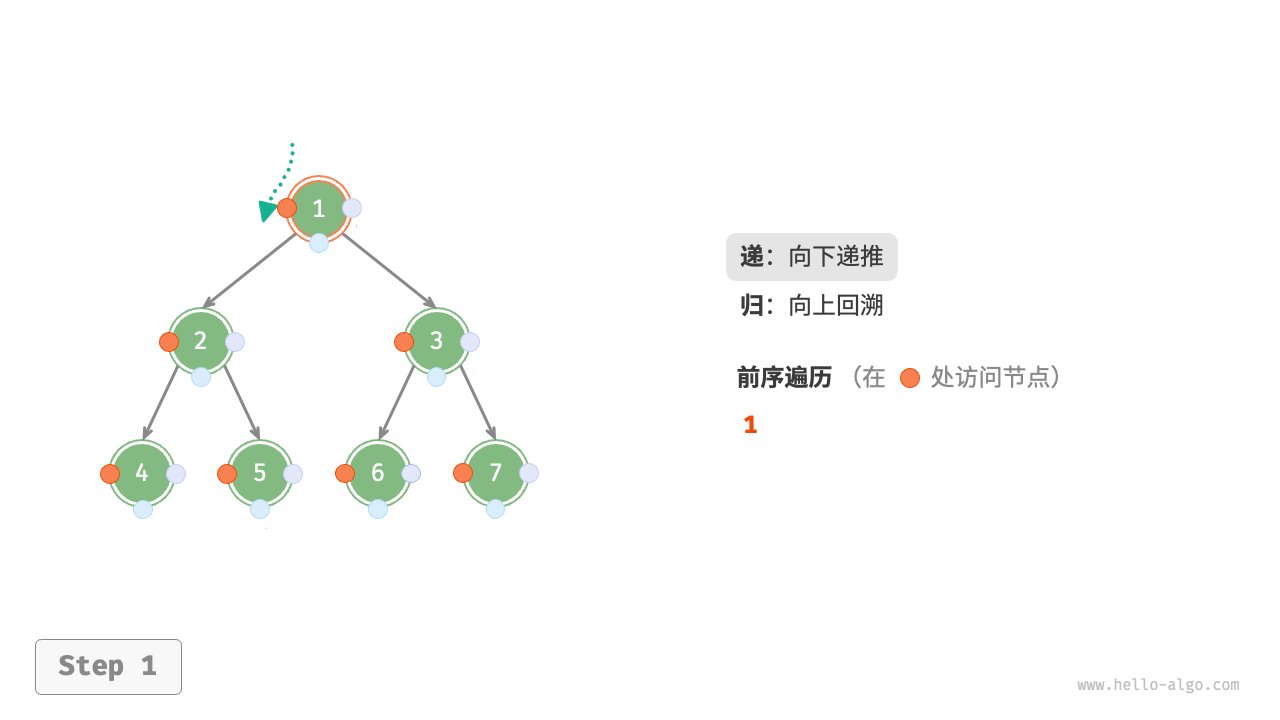
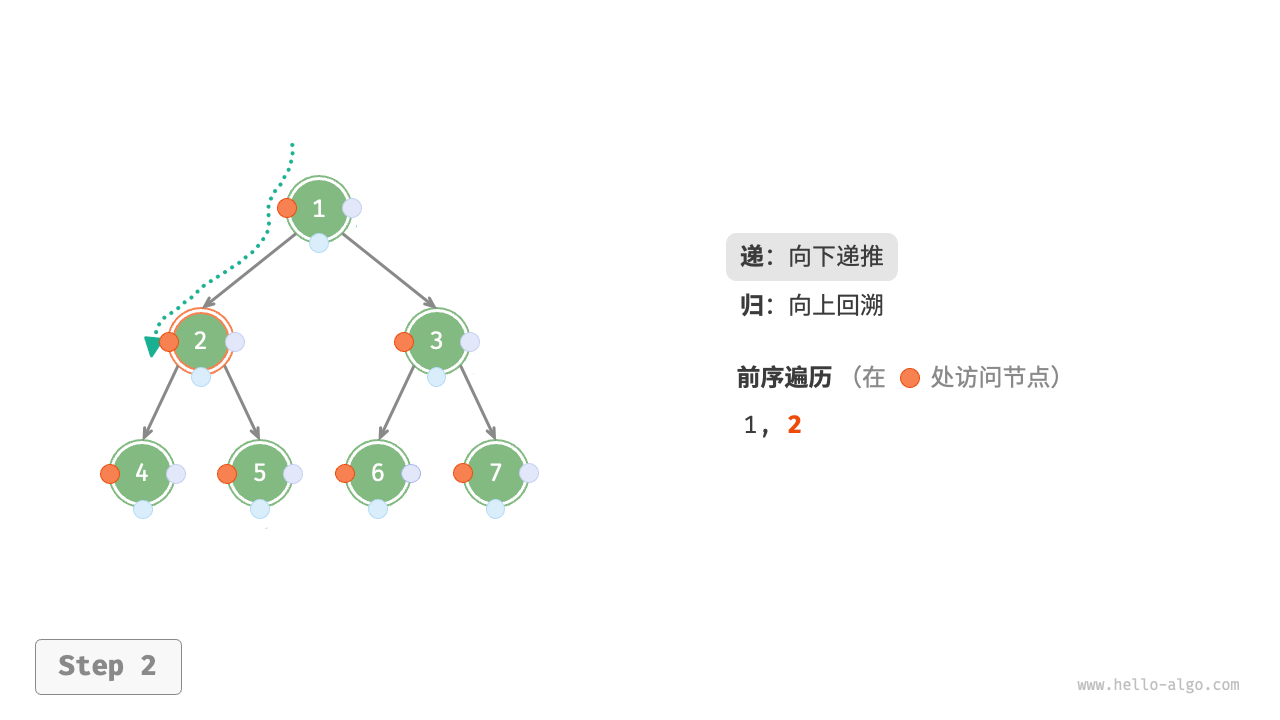
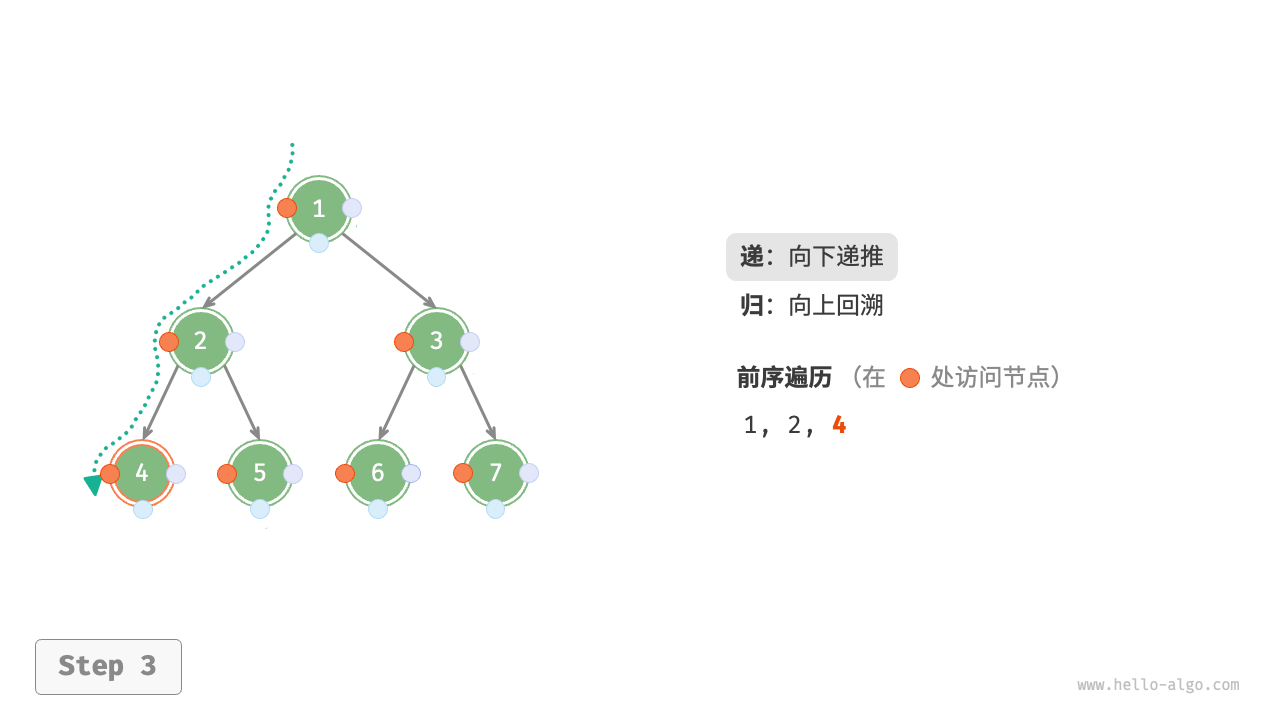
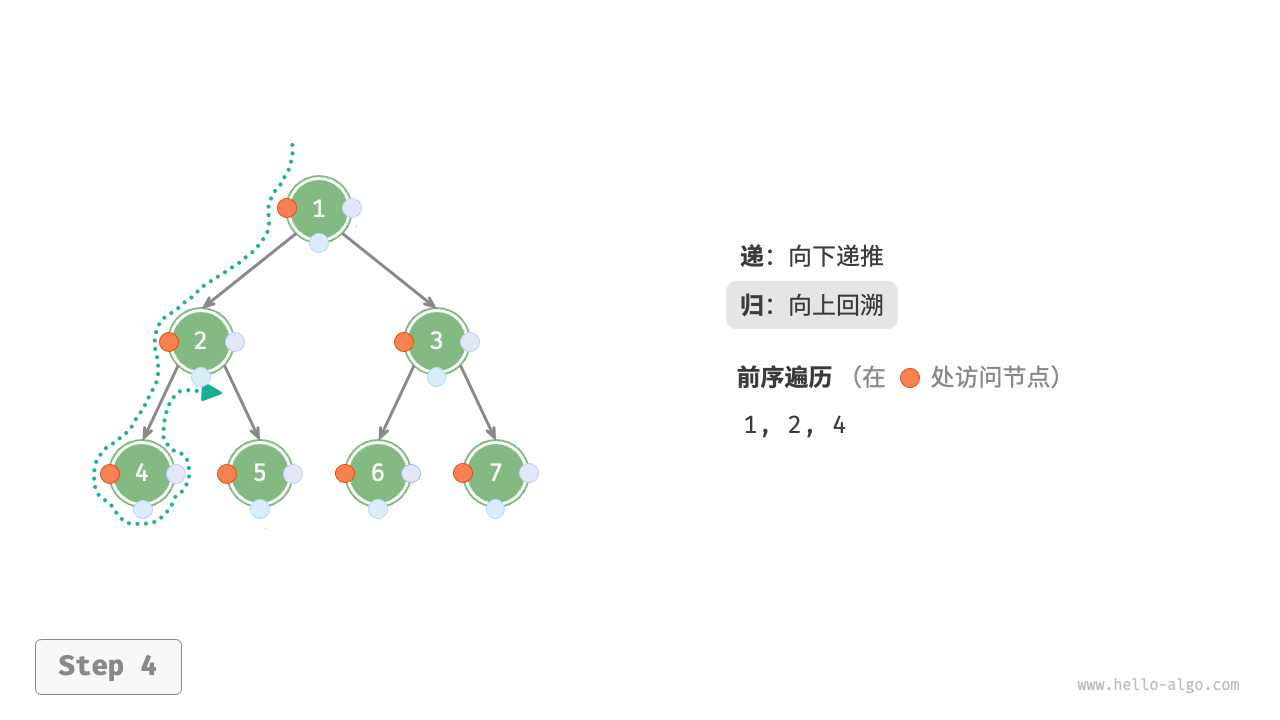
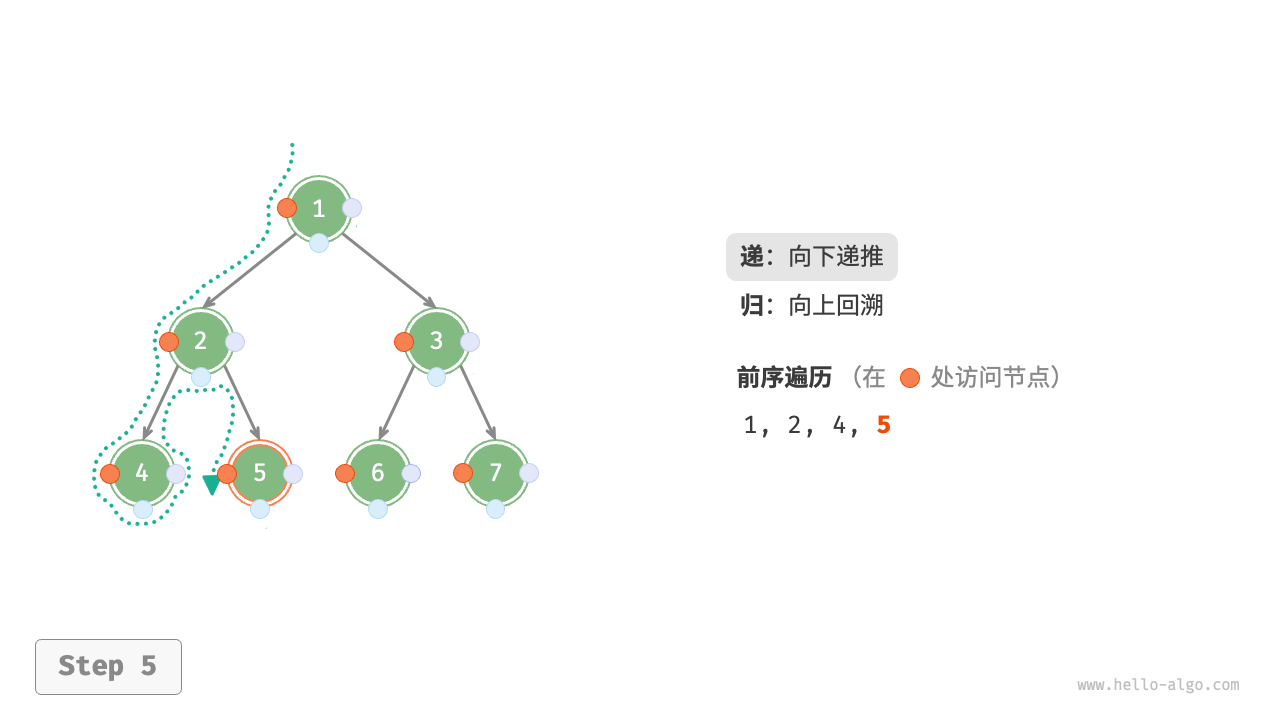
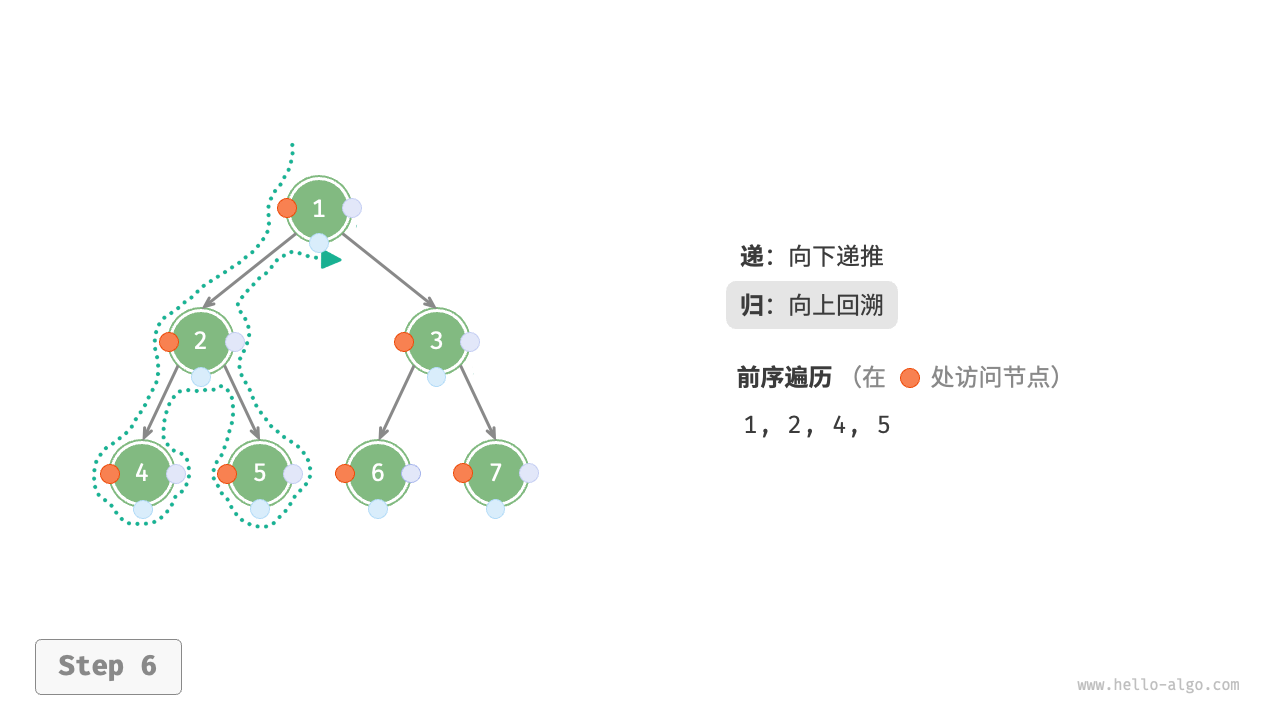
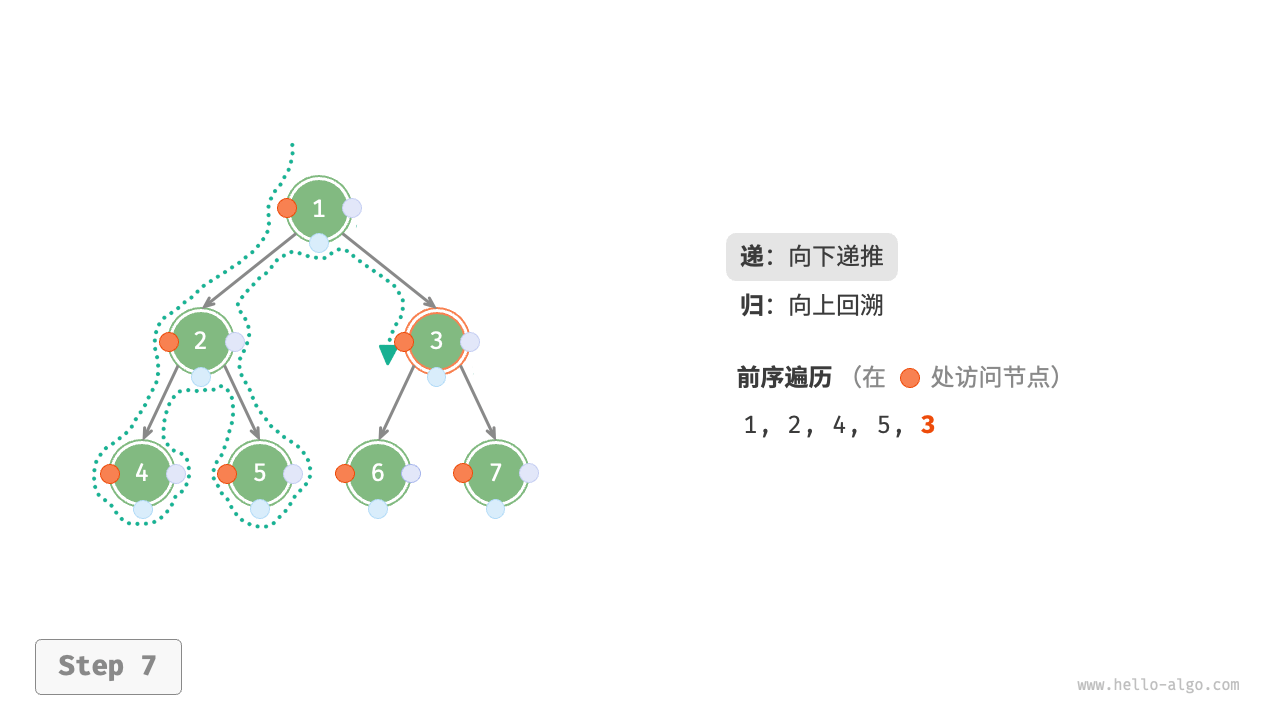
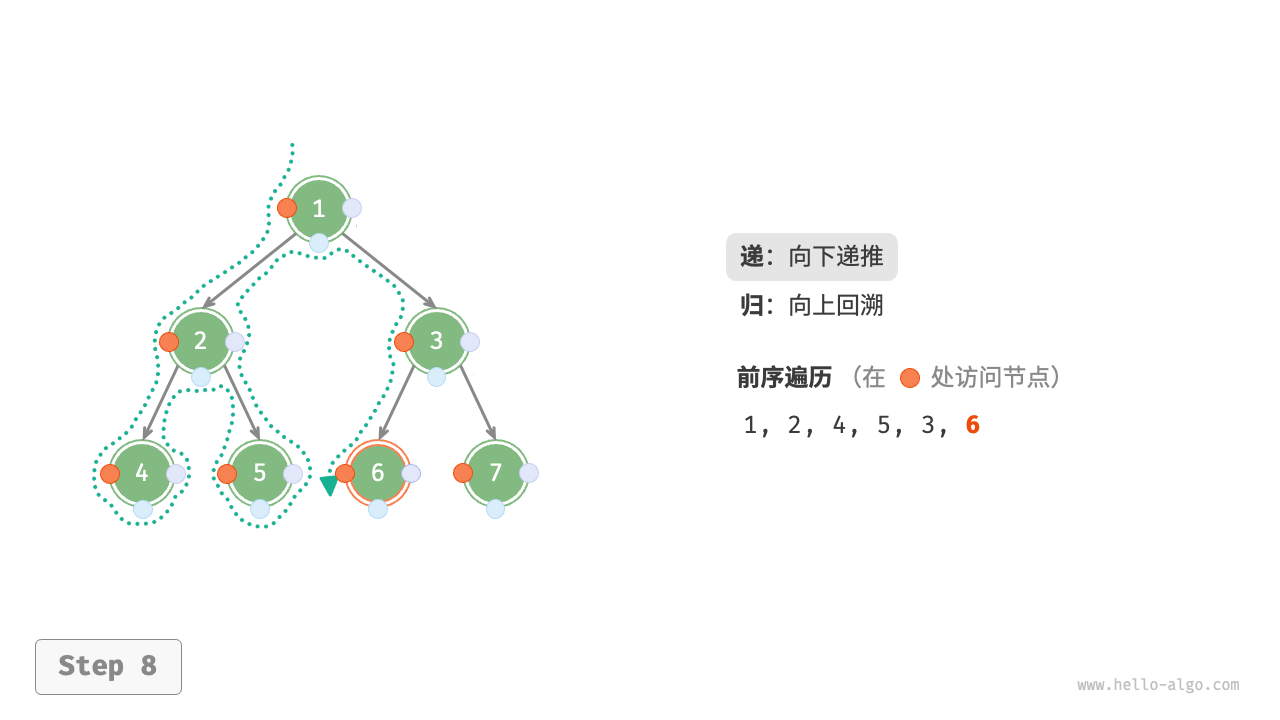
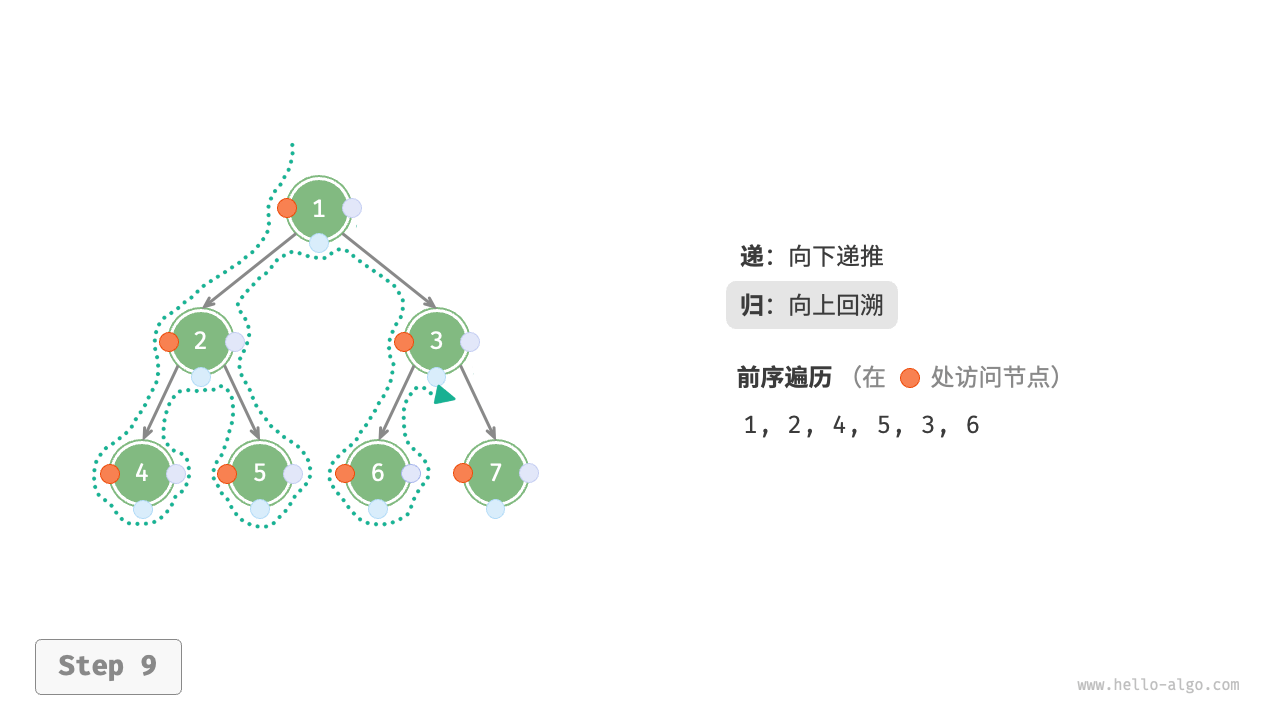
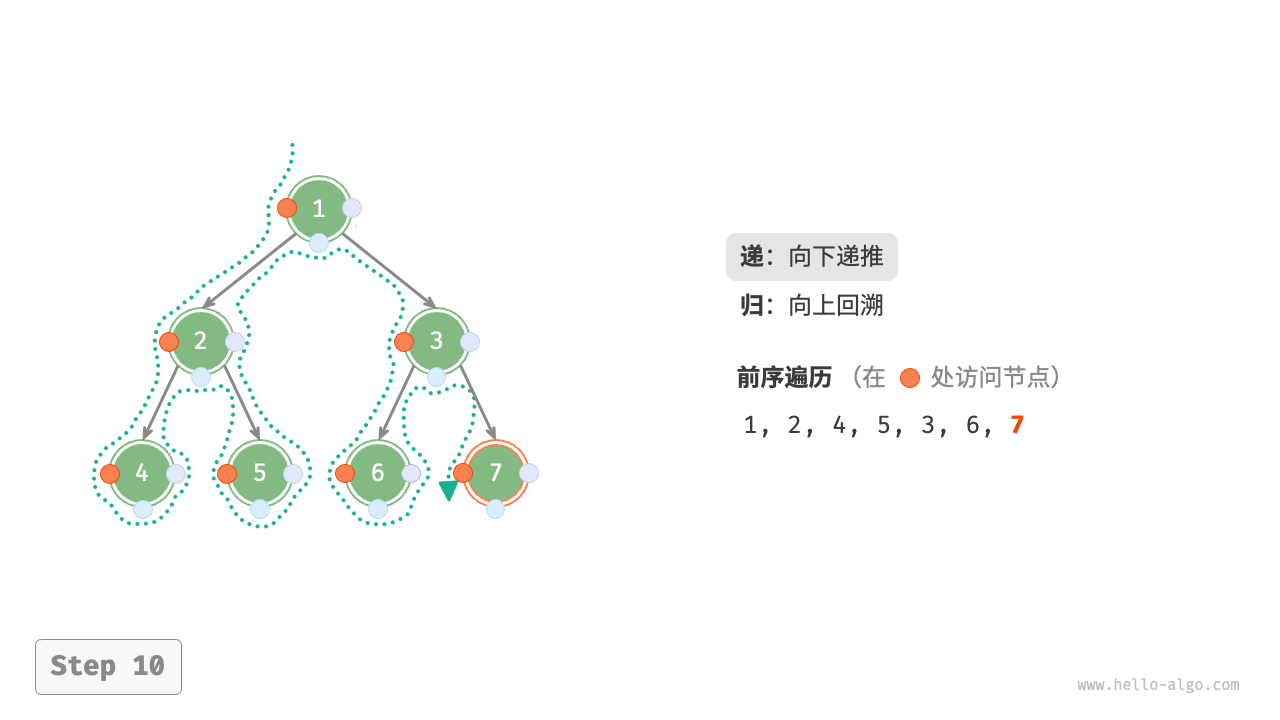
The Figure 7-11 shows the recursive process of preorder traversal of a binary tree, which can be divided into two opposite parts: "recursion" and "return".
- "Recursion" means starting a new method, the program accesses the next node in this process.
- "Return" means the function returns, indicating the current node has been fully accessed.
Figure 7-11 The recursive process of preorder traversal
2. Complexity analysis¶
- Time complexity is \(O(n)\): All nodes are visited once, using \(O(n)\) time.
- Space complexity is \(O(n)\): In the worst case, i.e., the tree degrades into a linked list, the recursion depth reaches \(n\), the system occupies \(O(n)\) stack frame space.