8.3 Top-k problem¶
Question
Given an unordered array nums of length \(n\), return the largest \(k\) elements in the array.
For this problem, we will first introduce two straightforward solutions, then explain a more efficient heap-based method.
8.3.1 Method 1: Iterative selection¶
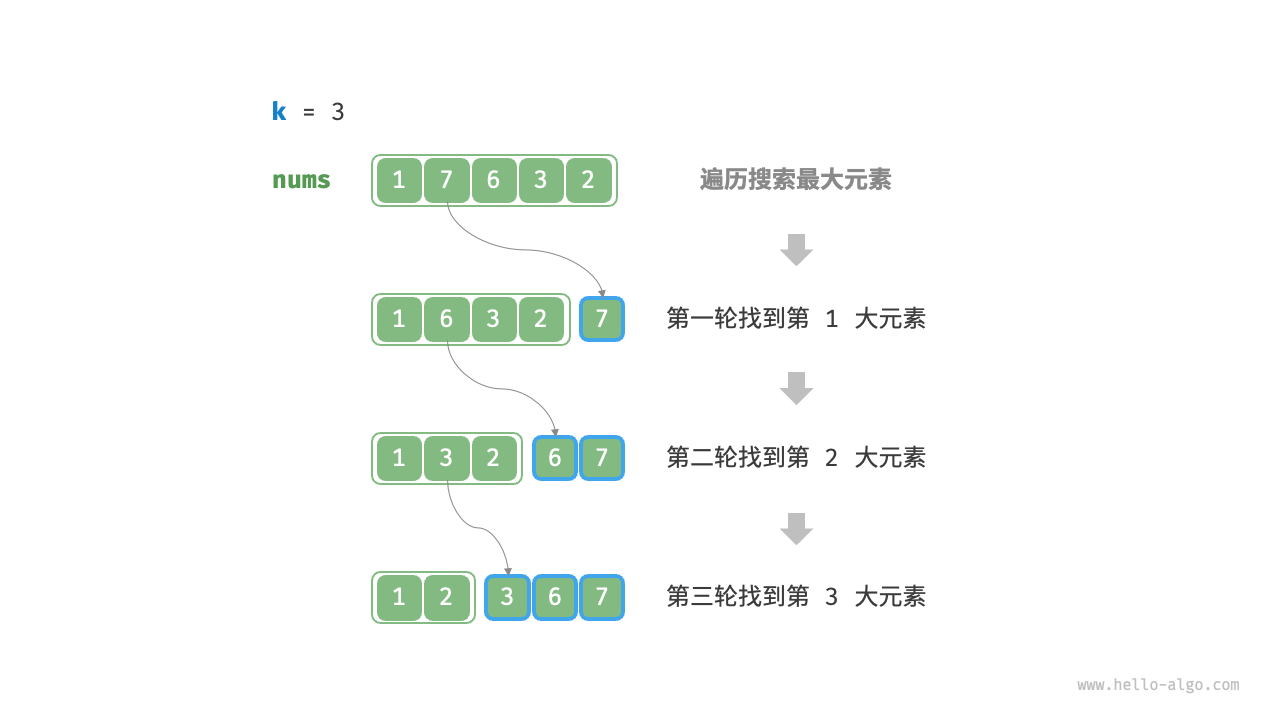
We can perform \(k\) rounds of iterations as shown in the Figure 8-6 , extracting the \(1^{st}\), \(2^{nd}\), \(\dots\), \(k^{th}\) largest elements in each round, with a time complexity of \(O(nk)\).
This method is only suitable when \(k \ll n\), as the time complexity approaches \(O(n^2)\) when \(k\) is close to \(n\), which is very time-consuming.
Figure 8-6 Iteratively finding the largest k elements
Tip
When \(k = n\), we can obtain a complete ordered sequence, which is equivalent to the "selection sort" algorithm.
8.3.2 Method 2: Sorting¶
As shown in the Figure 8-7 , we can first sort the array nums and then return the last \(k\) elements, with a time complexity of \(O(n \log n)\).
Clearly, this method "overachieves" the task, as we only need to find the largest \(k\) elements, without the need to sort the other elements.
Figure 8-7 Sorting to find the largest k elements
8.3.3 Method 3: Heap¶
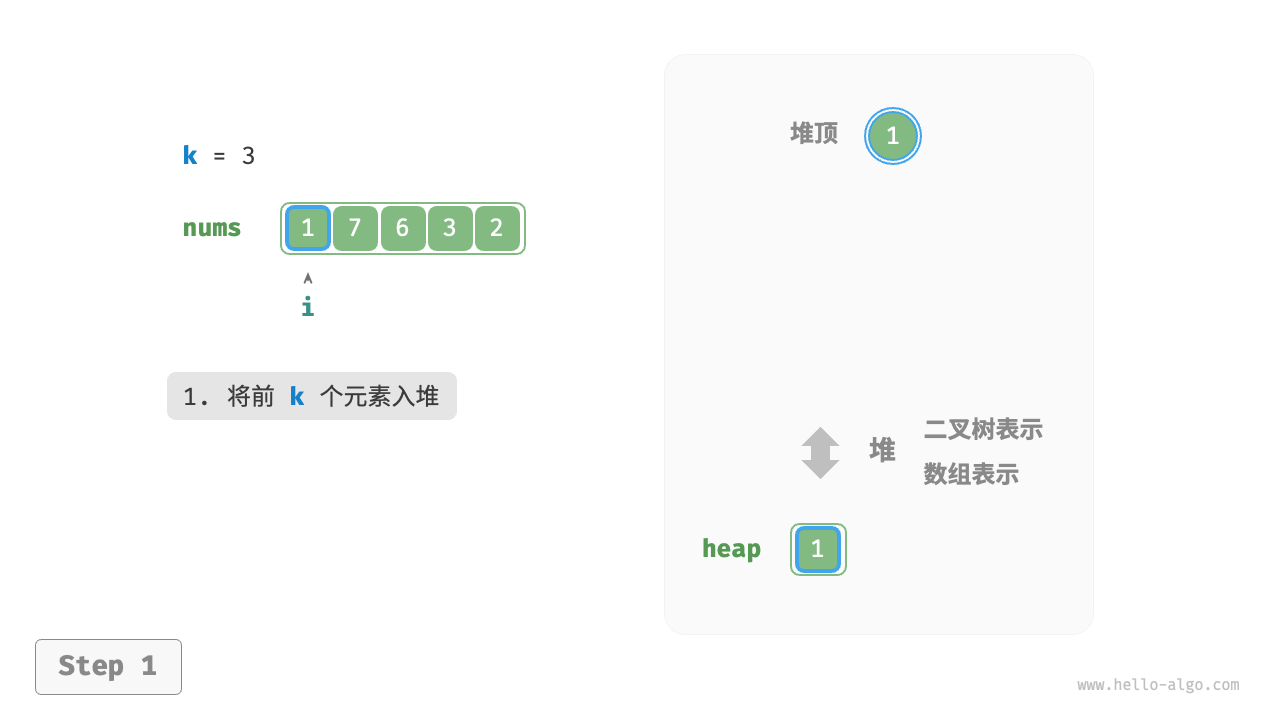
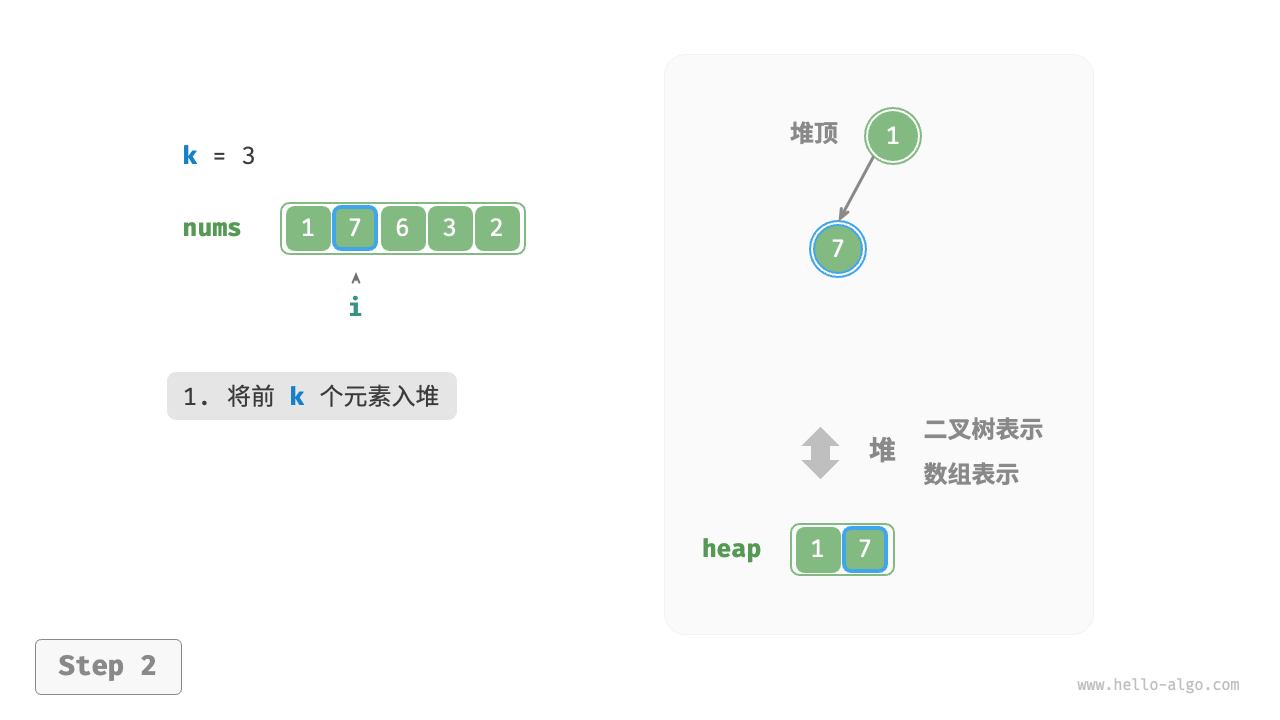
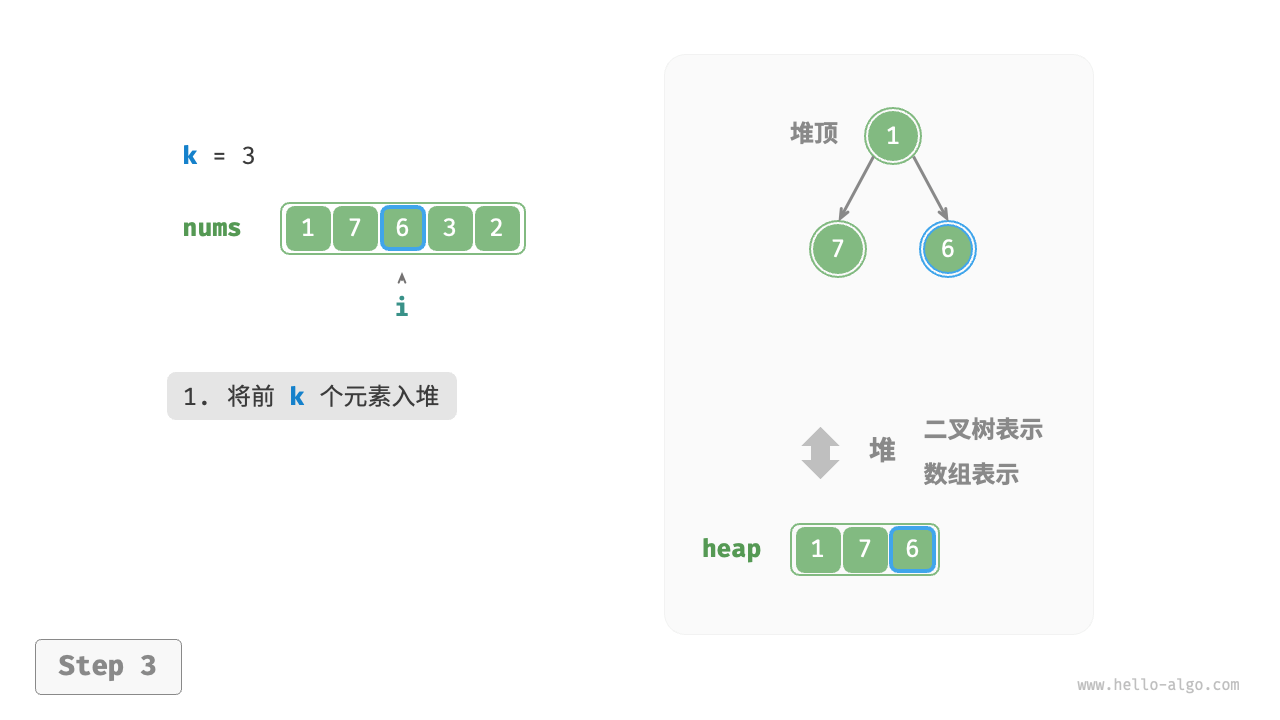
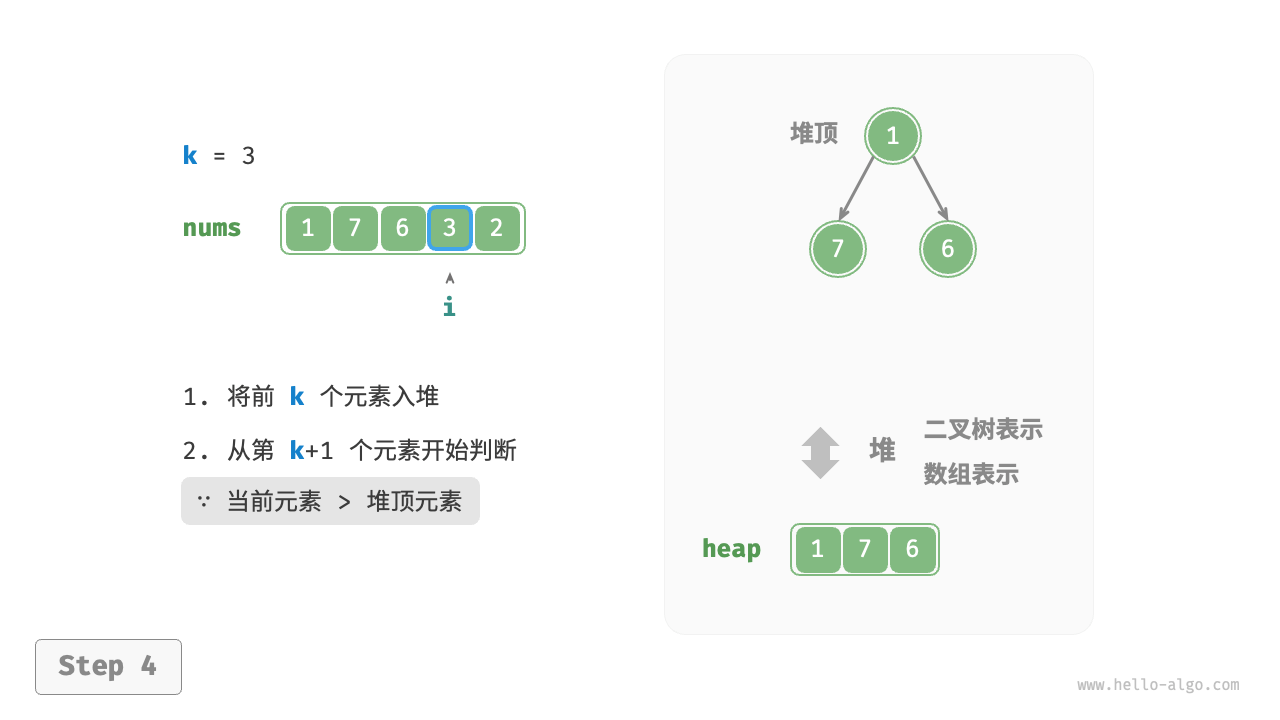
We can solve the Top-k problem more efficiently based on heaps, as shown in the following process.
- Initialize a min heap, where the top element is the smallest.
- First, insert the first \(k\) elements of the array into the heap.
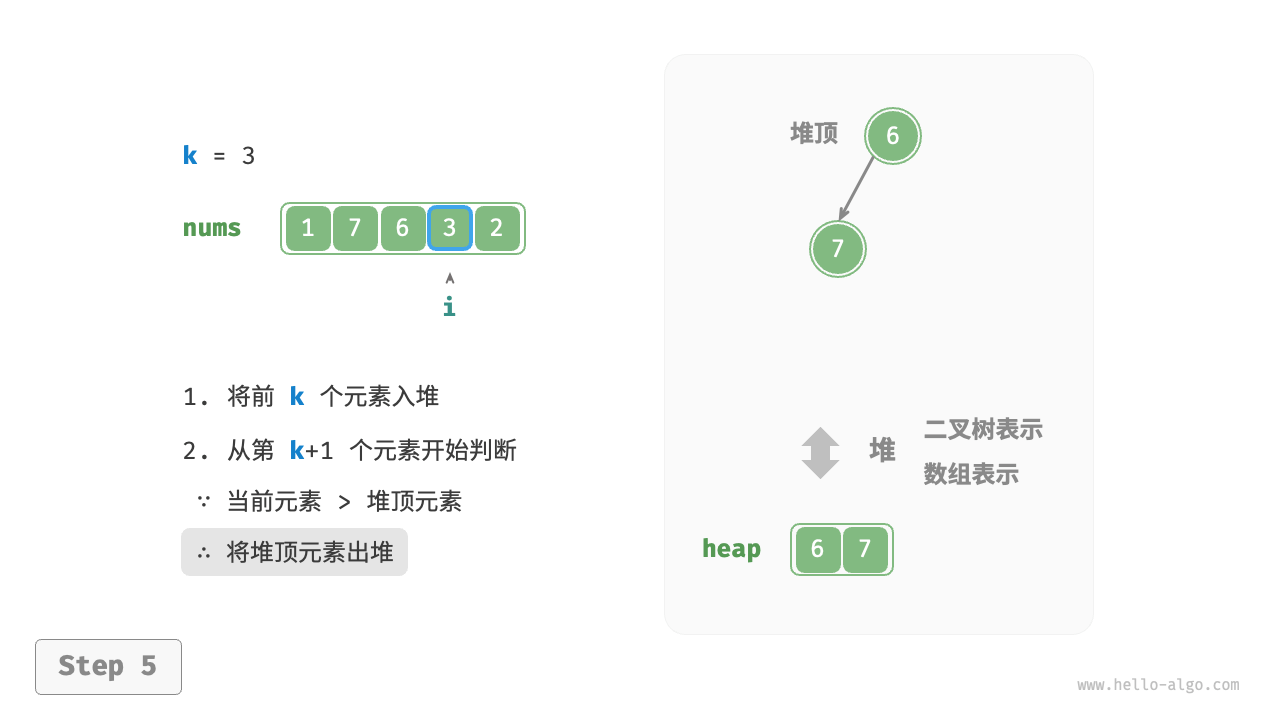
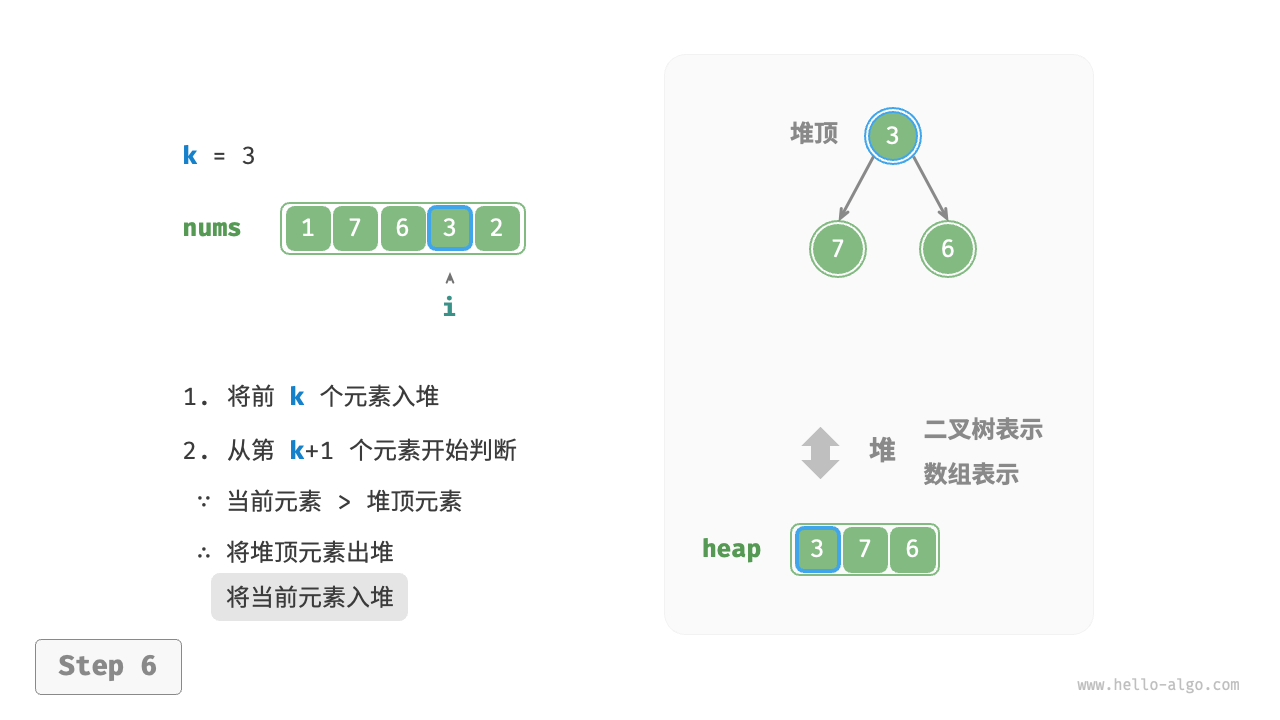
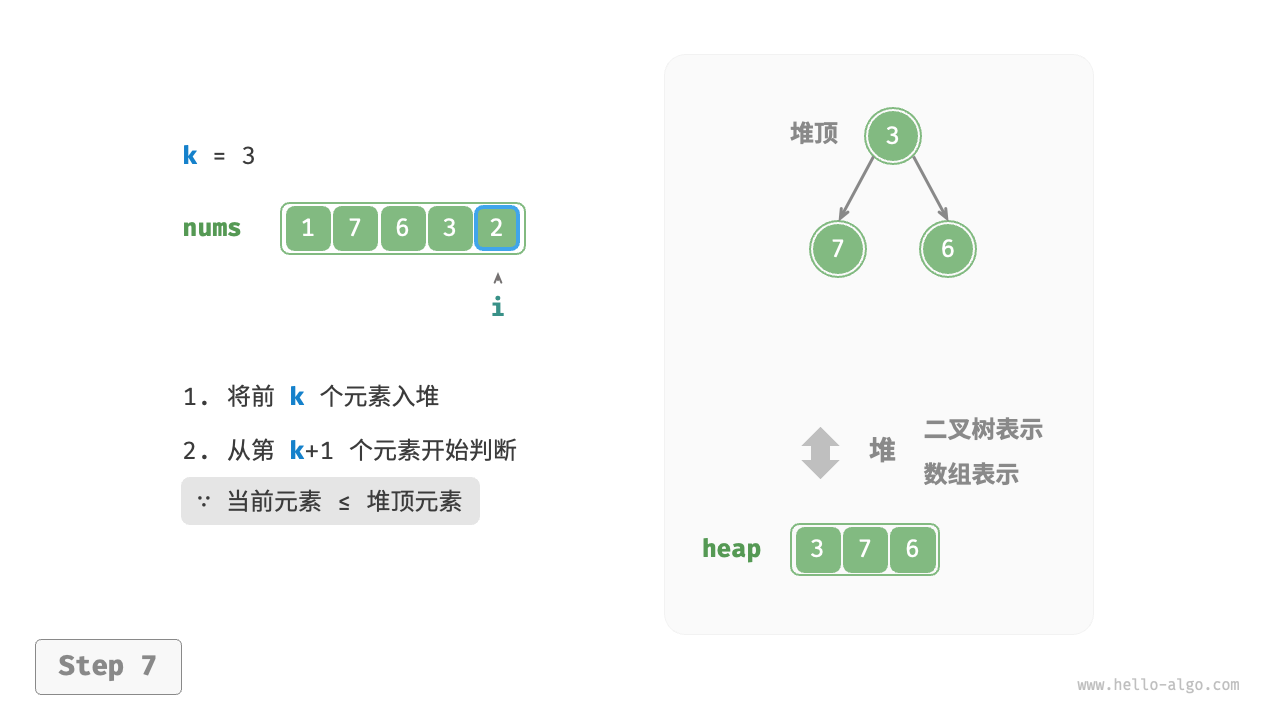
- Starting from the \(k + 1^{th}\) element, if the current element is greater than the top element of the heap, remove the top element of the heap and insert the current element into the heap.
- After completing the traversal, the heap contains the largest \(k\) elements.
Figure 8-8 Find the largest k elements based on heap
Example code is as follows:
def top_k_heap(nums: list[int], k: int) -> list[int]:
"""基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素"""
# 初始化小顶堆
heap = []
# 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for i in range(k):
heapq.heappush(heap, nums[i])
# 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for i in range(k, len(nums)):
# 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if nums[i] > heap[0]:
heapq.heappop(heap)
heapq.heappush(heap, nums[i])
return heap
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> topKHeap(vector<int> &nums, int k) {
// 初始化小顶堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> heap;
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
heap.push(nums[i]);
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > heap.top()) {
heap.pop();
heap.push(nums[i]);
}
}
return heap;
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
Queue<Integer> topKHeap(int[] nums, int k) {
// 初始化小顶堆
Queue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
heap.offer(nums[i]);
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > heap.peek()) {
heap.poll();
heap.offer(nums[i]);
}
}
return heap;
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
PriorityQueue<int, int> TopKHeap(int[] nums, int k) {
// 初始化小顶堆
PriorityQueue<int, int> heap = new();
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
heap.Enqueue(nums[i], nums[i]);
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (int i = k; i < nums.Length; i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > heap.Peek()) {
heap.Dequeue();
heap.Enqueue(nums[i], nums[i]);
}
}
return heap;
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
func topKHeap(nums []int, k int) *minHeap {
// 初始化小顶堆
h := &minHeap{}
heap.Init(h)
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
heap.Push(h, nums[i])
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for i := k; i < len(nums); i++ {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if nums[i] > h.Top().(int) {
heap.Pop(h)
heap.Push(h, nums[i])
}
}
return h
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
func topKHeap(nums: [Int], k: Int) -> [Int] {
// 初始化一个小顶堆,并将前 k 个元素建堆
var heap = Heap(nums.prefix(k))
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for i in nums.indices.dropFirst(k) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if nums[i] > heap.min()! {
_ = heap.removeMin()
heap.insert(nums[i])
}
}
return heap.unordered
}
/* 元素入堆 */
function pushMinHeap(maxHeap, val) {
// 元素取反
maxHeap.push(-val);
}
/* 元素出堆 */
function popMinHeap(maxHeap) {
// 元素取反
return -maxHeap.pop();
}
/* 访问堆顶元素 */
function peekMinHeap(maxHeap) {
// 元素取反
return -maxHeap.peek();
}
/* 取出堆中元素 */
function getMinHeap(maxHeap) {
// 元素取反
return maxHeap.getMaxHeap().map((num) => -num);
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
function topKHeap(nums, k) {
// 初始化小顶堆
// 请注意:我们将堆中所有元素取反,从而用大顶堆来模拟小顶堆
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap([]);
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pushMinHeap(maxHeap, nums[i]);
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (let i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > peekMinHeap(maxHeap)) {
popMinHeap(maxHeap);
pushMinHeap(maxHeap, nums[i]);
}
}
// 返回堆中元素
return getMinHeap(maxHeap);
}
/* 元素入堆 */
function pushMinHeap(maxHeap: MaxHeap, val: number): void {
// 元素取反
maxHeap.push(-val);
}
/* 元素出堆 */
function popMinHeap(maxHeap: MaxHeap): number {
// 元素取反
return -maxHeap.pop();
}
/* 访问堆顶元素 */
function peekMinHeap(maxHeap: MaxHeap): number {
// 元素取反
return -maxHeap.peek();
}
/* 取出堆中元素 */
function getMinHeap(maxHeap: MaxHeap): number[] {
// 元素取反
return maxHeap.getMaxHeap().map((num: number) => -num);
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
function topKHeap(nums: number[], k: number): number[] {
// 初始化小顶堆
// 请注意:我们将堆中所有元素取反,从而用大顶堆来模拟小顶堆
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap([]);
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pushMinHeap(maxHeap, nums[i]);
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (let i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > peekMinHeap(maxHeap)) {
popMinHeap(maxHeap);
pushMinHeap(maxHeap, nums[i]);
}
}
// 返回堆中元素
return getMinHeap(maxHeap);
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
MinHeap topKHeap(List<int> nums, int k) {
// 初始化小顶堆,将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
MinHeap heap = MinHeap(nums.sublist(0, k));
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > heap.peek()) {
heap.pop();
heap.push(nums[i]);
}
}
return heap;
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
fn top_k_heap(nums: Vec<i32>, k: usize) -> BinaryHeap<Reverse<i32>> {
// BinaryHeap 是大顶堆,使用 Reverse 将元素取反,从而实现小顶堆
let mut heap = BinaryHeap::<Reverse<i32>>::new();
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for &num in nums.iter().take(k) {
heap.push(Reverse(num));
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for &num in nums.iter().skip(k) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if num > heap.peek().unwrap().0 {
heap.pop();
heap.push(Reverse(num));
}
}
heap
}
/* 元素入堆 */
void pushMinHeap(MaxHeap *maxHeap, int val) {
// 元素取反
push(maxHeap, -val);
}
/* 元素出堆 */
int popMinHeap(MaxHeap *maxHeap) {
// 元素取反
return -pop(maxHeap);
}
/* 访问堆顶元素 */
int peekMinHeap(MaxHeap *maxHeap) {
// 元素取反
return -peek(maxHeap);
}
/* 取出堆中元素 */
int *getMinHeap(MaxHeap *maxHeap) {
// 将堆中所有元素取反并存入 res 数组
int *res = (int *)malloc(maxHeap->size * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < maxHeap->size; i++) {
res[i] = -maxHeap->data[i];
}
return res;
}
/* 取出堆中元素 */
int *getMinHeap(MaxHeap *maxHeap) {
// 将堆中所有元素取反并存入 res 数组
int *res = (int *)malloc(maxHeap->size * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < maxHeap->size; i++) {
res[i] = -maxHeap->data[i];
}
return res;
}
// 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素的函数
int *topKHeap(int *nums, int sizeNums, int k) {
// 初始化小顶堆
// 请注意:我们将堆中所有元素取反,从而用大顶堆来模拟小顶堆
int *empty = (int *)malloc(0);
MaxHeap *maxHeap = newMaxHeap(empty, 0);
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pushMinHeap(maxHeap, nums[i]);
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (int i = k; i < sizeNums; i++) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > peekMinHeap(maxHeap)) {
popMinHeap(maxHeap);
pushMinHeap(maxHeap, nums[i]);
}
}
int *res = getMinHeap(maxHeap);
// 释放内存
delMaxHeap(maxHeap);
return res;
}
/* 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 */
fun topKHeap(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Queue<Int> {
// 初始化小顶堆
val heap = PriorityQueue<Int>()
// 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for (i in 0..<k) {
heap.offer(nums[i])
}
// 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for (i in k..<nums.size) {
// 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if (nums[i] > heap.peek()) {
heap.poll()
heap.offer(nums[i])
}
}
return heap
}
### 基于堆查找数组中最大的 k 个元素 ###
def top_k_heap(nums, k)
# 初始化小顶堆
# 请注意:我们将堆中所有元素取反,从而用大顶堆来模拟小顶堆
max_heap = MaxHeap.new([])
# 将数组的前 k 个元素入堆
for i in 0...k
push_min_heap(max_heap, nums[i])
end
# 从第 k+1 个元素开始,保持堆的长度为 k
for i in k...nums.length
# 若当前元素大于堆顶元素,则将堆顶元素出堆、当前元素入堆
if nums[i] > peek_min_heap(max_heap)
pop_min_heap(max_heap)
push_min_heap(max_heap, nums[i])
end
end
get_min_heap(max_heap)
end
Code Visualization
A total of \(n\) rounds of heap insertions and deletions are performed, with the maximum heap size being \(k\), hence the time complexity is \(O(n \log k)\). This method is very efficient; when \(k\) is small, the time complexity tends towards \(O(n)\); when \(k\) is large, the time complexity will not exceed \(O(n \log n)\).
Additionally, this method is suitable for scenarios with dynamic data streams. By continuously adding data, we can maintain the elements within the heap, thereby achieving dynamic updates of the largest \(k\) elements.