9.2. 图基础操作¶
图的基础操作分为对「边」的操作和对「顶点」的操作,在「邻接矩阵」和「邻接表」这两种表示下的实现方式不同。
9.2.1. 基于邻接矩阵的实现¶
设图的顶点总数为 \(n\) ,则有:
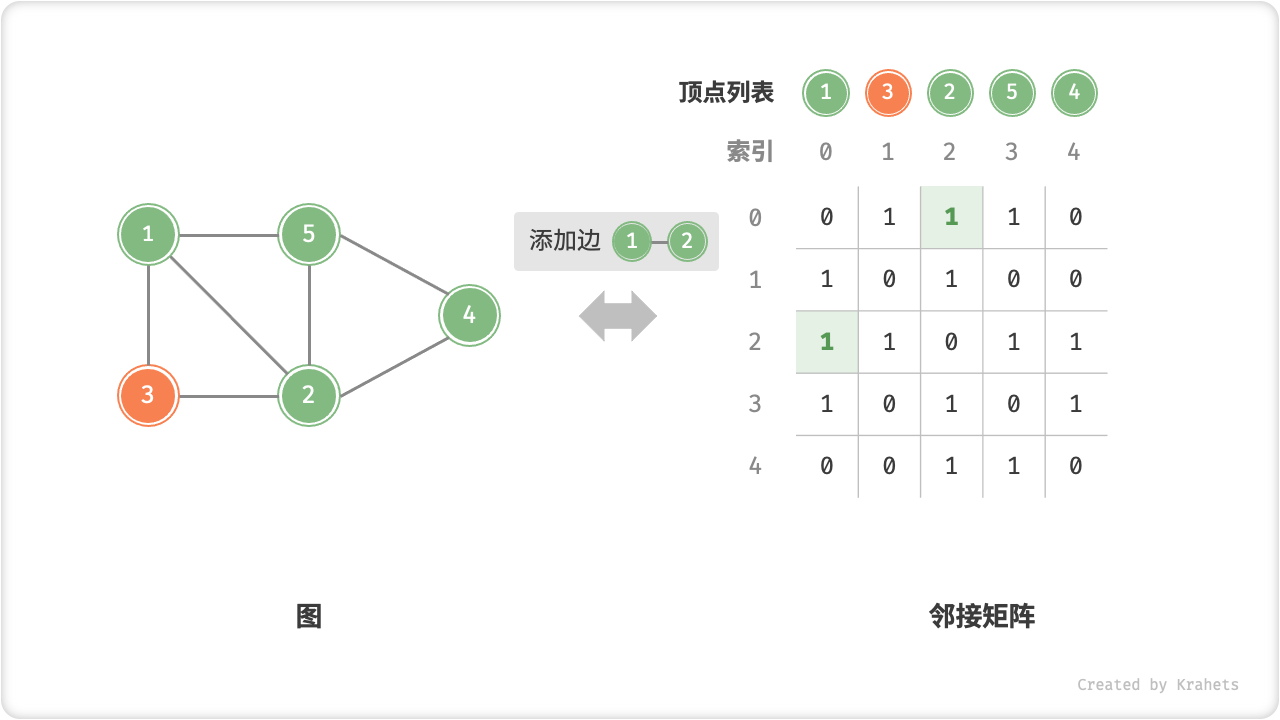
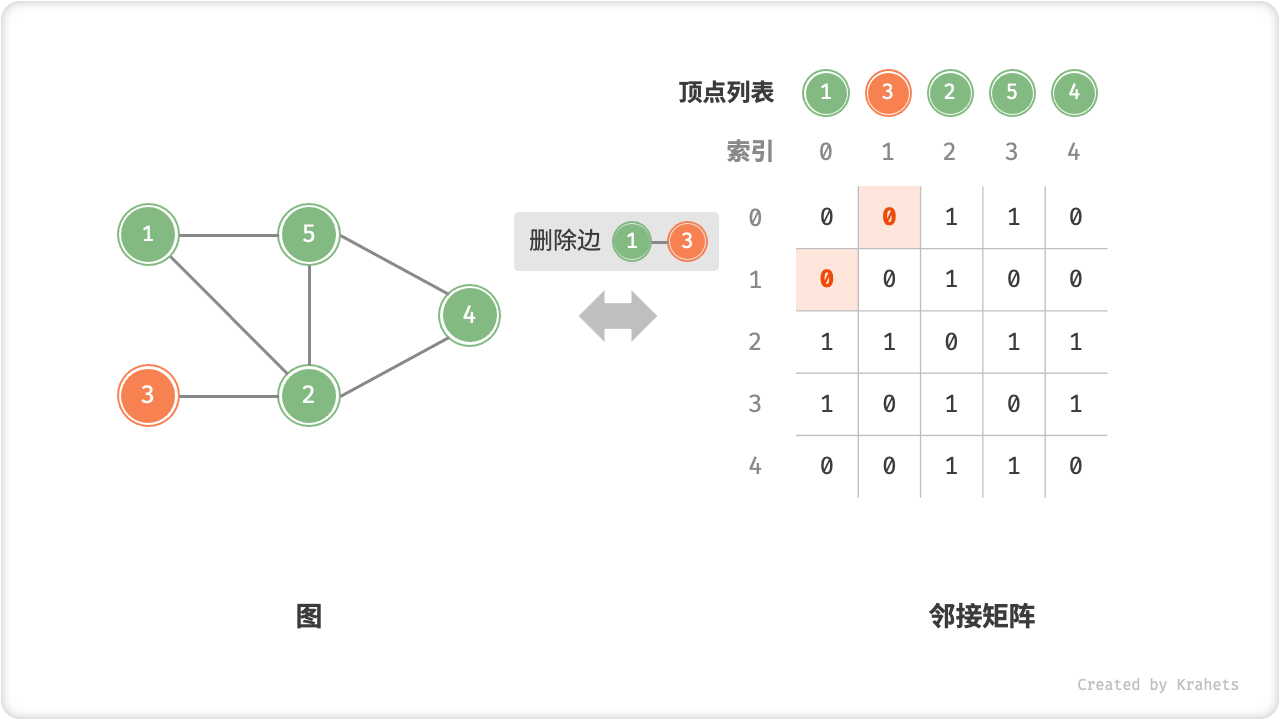
- 添加或删除边:直接在邻接矩阵中修改指定边的对应元素即可,使用 \(O(1)\) 时间。而由于是无向图,因此需要同时更新两个方向的边。
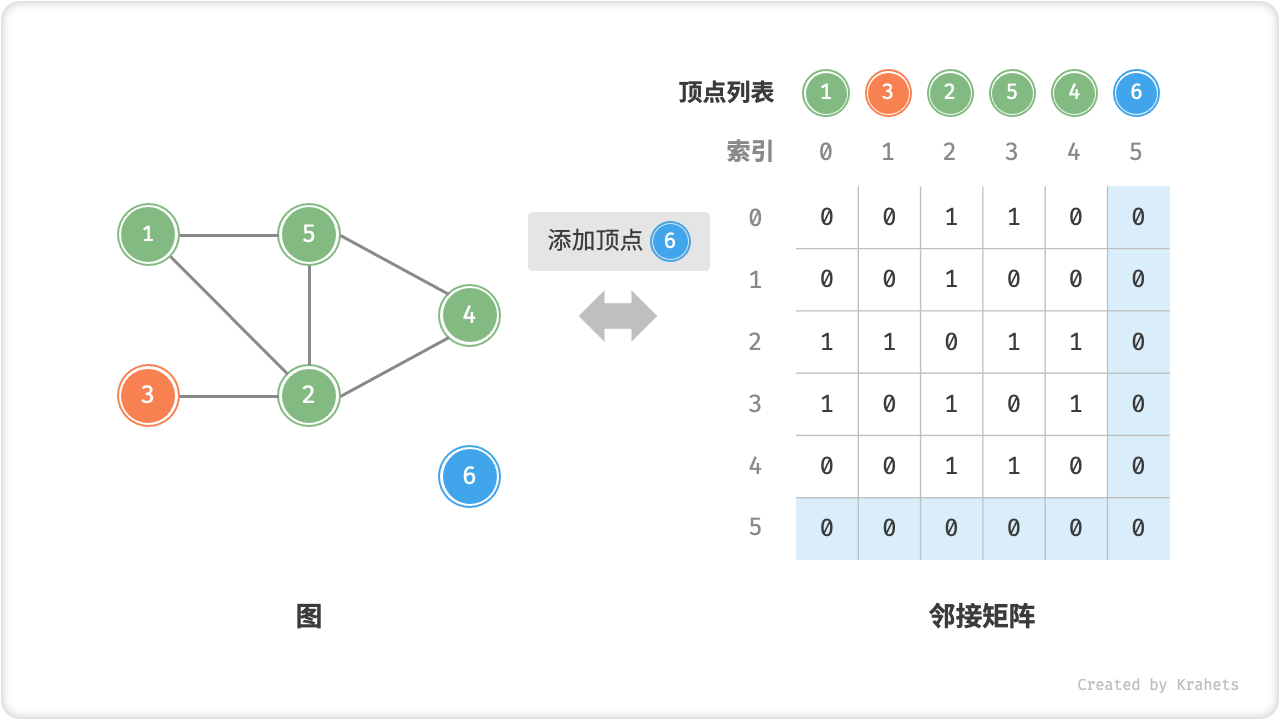
- 添加顶点:在邻接矩阵的尾部添加一行一列,并全部填 \(0\) 即可,使用 \(O(n)\) 时间。
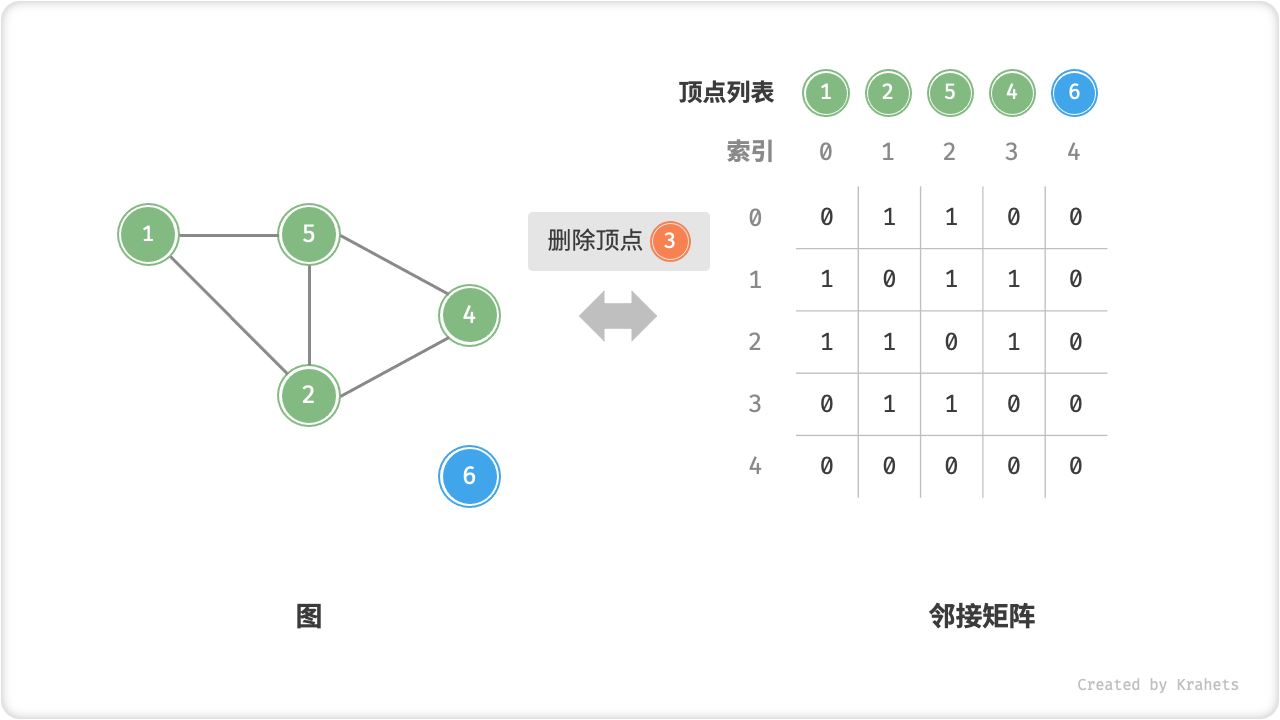
- 删除顶点:在邻接矩阵中删除一行一列。当删除首行首列时达到最差情况,需要将 \((n-1)^2\) 个元素“向左上移动”,从而使用 \(O(n^2)\) 时间。
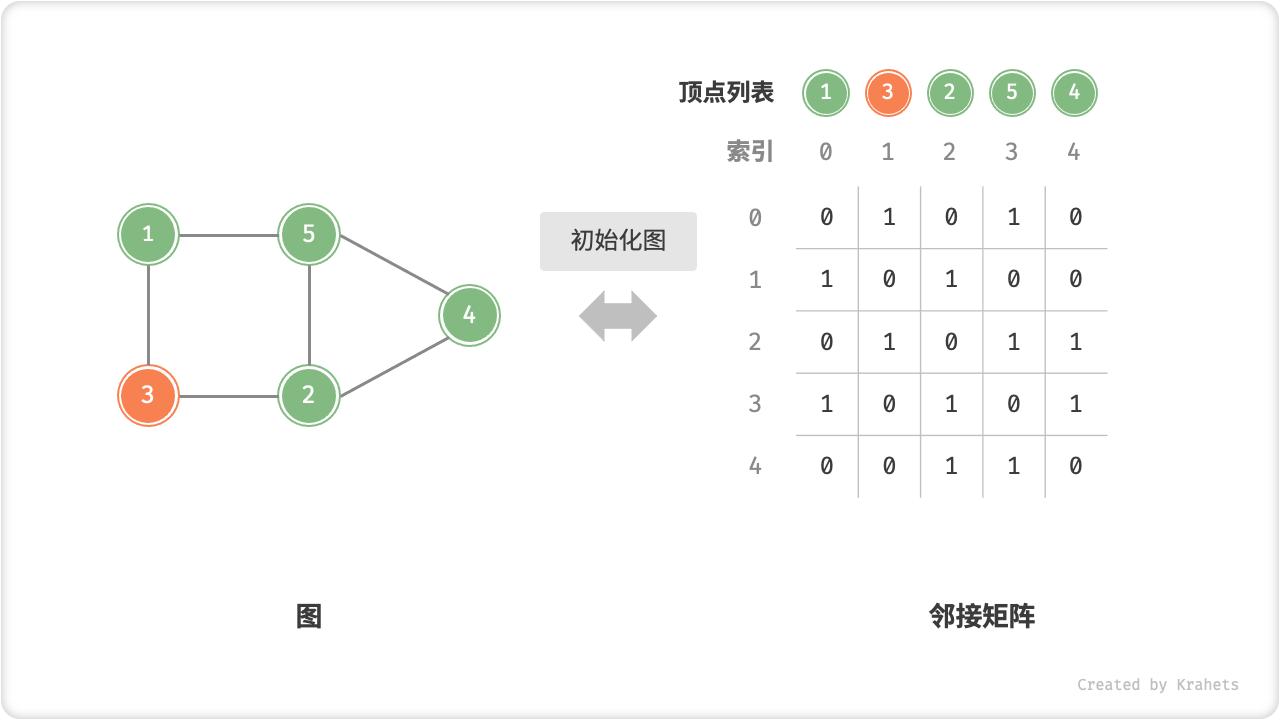
- 初始化:传入 \(n\) 个顶点,初始化长度为 \(n\) 的顶点列表
vertices,使用 \(O(n)\) 时间;初始化 \(n \times n\) 大小的邻接矩阵adjMat,使用 \(O(n^2)\) 时间。
以下是基于邻接矩阵表示图的实现代码。
graph_adjacency_matrix.java
/* 基于邻接矩阵实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjMat {
List<Integer> vertices; // 顶点列表,元素代表“顶点值”,索引代表“顶点索引”
List<List<Integer>> adjMat; // 邻接矩阵,行列索引对应“顶点索引”
/* 构造方法 */
public GraphAdjMat(int[] vertices, int[][] edges) {
this.vertices = new ArrayList<>();
this.adjMat = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加顶点
for (int val : vertices) {
addVertex(val);
}
// 添加边
// 请注意,edges 元素代表顶点索引,即对应 vertices 元素索引
for (int[] e : edges) {
addEdge(e[0], e[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
public int size() {
return vertices.size();
}
/* 添加顶点 */
public void addVertex(int val) {
int n = size();
// 向顶点列表中添加新顶点的值
vertices.add(val);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一行
List<Integer> newRow = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
newRow.add(0);
}
adjMat.add(newRow);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一列
for (List<Integer> row : adjMat) {
row.add(0);
}
}
/* 删除顶点 */
public void removeVertex(int index) {
if (index >= size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
// 在顶点列表中移除索引 index 的顶点
vertices.remove(index);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的行
adjMat.remove(index);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的列
for (List<Integer> row : adjMat) {
row.remove(index);
}
}
/* 添加边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
public void addEdge(int i, int j) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= size() || j >= size() || i == j)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
// 在无向图中,邻接矩阵沿主对角线对称,即满足 (i, j) == (j, i)
adjMat.get(i).set(j, 1);
adjMat.get(j).set(i, 1);
}
/* 删除边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
public void removeEdge(int i, int j) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= size() || j >= size() || i == j)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
adjMat.get(i).set(j, 0);
adjMat.get(j).set(i, 0);
}
/* 打印邻接矩阵 */
public void print() {
System.out.print("顶点列表 = ");
System.out.println(vertices);
System.out.println("邻接矩阵 =");
PrintUtil.printMatrix(adjMat);
}
}
graph_adjacency_matrix.cpp
/* 基于邻接矩阵实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjMat {
vector<int> vertices; // 顶点列表,元素代表“顶点值”,索引代表“顶点索引”
vector<vector<int>> adjMat; // 邻接矩阵,行列索引对应“顶点索引”
public:
/* 构造方法 */
GraphAdjMat(const vector<int>& vertices, const vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
// 添加顶点
for (int val : vertices) {
addVertex(val);
}
// 添加边
// 请注意,edges 元素代表顶点索引,即对应 vertices 元素索引
for (const vector<int>& edge : edges) {
addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
int size() const {
return vertices.size();
}
/* 添加顶点 */
void addVertex(int val) {
int n = size();
// 向顶点列表中添加新顶点的值
vertices.push_back(val);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一行
adjMat.emplace_back(n, 0);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一列
for (vector<int>& row : adjMat) {
row.push_back(0);
}
}
/* 删除顶点 */
void removeVertex(int index) {
if (index >= size()) {
throw out_of_range("顶点不存在");
}
// 在顶点列表中移除索引 index 的顶点
vertices.erase(vertices.begin() + index);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的行
adjMat.erase(adjMat.begin() + index);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的列
for (vector<int>& row : adjMat) {
row.erase(row.begin() + index);
}
}
/* 添加边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
void addEdge(int i, int j) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= size() || j >= size() || i == j) {
throw out_of_range("顶点不存在");
}
// 在无向图中,邻接矩阵沿主对角线对称,即满足 (i, j) == (j, i)
adjMat[i][j] = 1;
adjMat[j][i] = 1;
}
/* 删除边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
void removeEdge(int i, int j) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= size() || j >= size() || i == j) {
throw out_of_range("顶点不存在");
}
adjMat[i][j] = 0;
adjMat[j][i] = 0;
}
/* 打印邻接矩阵 */
void print() {
cout << "顶点列表 = ";
PrintUtil::printVector(vertices);
cout << "邻接矩阵 =" << endl;
PrintUtil::printVectorMatrix(adjMat);
}
};
graph_adjacency_matrix.go
/* 基于邻接矩阵实现的无向图类 */
type graphAdjMat struct {
// 顶点列表,元素代表“顶点值”,索引代表“顶点索引”
vertices []int
// 邻接矩阵,行列索引对应“顶点索引”
adjMat [][]int
}
/* 构造方法 */
func newGraphAdjMat(vertices []int, edges [][]int) *graphAdjMat {
// 添加顶点
n := len(vertices)
adjMat := make([][]int, n)
for i := range adjMat {
adjMat[i] = make([]int, n)
}
// 初始化图
g := &graphAdjMat{
vertices: vertices,
adjMat: adjMat,
}
// 添加边
// 请注意,edges 元素代表顶点索引,即对应 vertices 元素索引
for i := range edges {
g.addEdge(edges[i][0], edges[i][1])
}
return g
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
func (g *graphAdjMat) size() int {
return len(g.vertices)
}
/* 添加顶点 */
func (g *graphAdjMat) addVertex(val int) {
n := g.size()
// 向顶点列表中添加新顶点的值
g.vertices = append(g.vertices, val)
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一行
newRow := make([]int, n)
g.adjMat = append(g.adjMat, newRow)
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一列
for i := range g.adjMat {
g.adjMat[i] = append(g.adjMat[i], 0)
}
}
/* 删除顶点 */
func (g *graphAdjMat) removeVertex(index int) {
if index >= g.size() {
return
}
// 在顶点列表中移除索引 index 的顶点
g.vertices = append(g.vertices[:index], g.vertices[index+1:]...)
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的行
g.adjMat = append(g.adjMat[:index], g.adjMat[index+1:]...)
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的列
for i := range g.adjMat {
g.adjMat[i] = append(g.adjMat[i][:index], g.adjMat[i][index+1:]...)
}
}
/* 添加边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
func (g *graphAdjMat) addEdge(i, j int) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= g.size() || j >= g.size() || i == j {
fmt.Errorf("%s", "Index Out Of Bounds Exception")
}
// 在无向图中,邻接矩阵沿主对角线对称,即满足 (i, j) == (j, i)
g.adjMat[i][j] = 1
g.adjMat[j][i] = 1
}
/* 删除边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
func (g *graphAdjMat) removeEdge(i, j int) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= g.size() || j >= g.size() || i == j {
fmt.Errorf("%s", "Index Out Of Bounds Exception")
}
g.adjMat[i][j] = 0
g.adjMat[j][i] = 0
}
/* 打印邻接矩阵 */
func (g *graphAdjMat) print() {
fmt.Printf("\t顶点列表 = %v\n", g.vertices)
fmt.Printf("\t邻接矩阵 = \n")
for i := range g.adjMat {
fmt.Printf("\t\t\t%v\n", g.adjMat[i])
}
}
graph_adjacency_matrix.js
/* 基于邻接矩阵实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjMat {
vertices; // 顶点列表,元素代表“顶点值”,索引代表“顶点索引”
adjMat; // 邻接矩阵,行列索引对应“顶点索引”
/* 构造函数 */
constructor(vertices, edges) {
this.vertices = [];
this.adjMat = [];
// 添加顶点
for (const val of vertices) {
this.addVertex(val);
}
// 添加边
// 请注意,edges 元素代表顶点索引,即对应 vertices 元素索引
for (const e of edges) {
this.addEdge(e[0], e[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
size() {
return this.vertices.length;
}
/* 添加顶点 */
addVertex(val) {
const n = this.size();
// 向顶点列表中添加新顶点的值
this.vertices.push(val);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一行
const newRow = [];
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
newRow.push(0);
}
this.adjMat.push(newRow);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一列
for (const row of this.adjMat) {
row.push(0);
}
}
/* 删除顶点 */
removeVertex(index) {
if (index >= this.size()) {
throw new RangeError("Index Out Of Bounds Exception");
}
// 在顶点列表中移除索引 index 的顶点
this.vertices.splice(index, 1);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的行
this.adjMat.splice(index, 1);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的列
for (const row of this.adjMat) {
row.splice(index, 1);
}
}
/* 添加边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
addEdge(i, j) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= this.size() || j >= this.size() || i === j) {
throw new RangeError("Index Out Of Bounds Exception");
}
// 在无向图中,邻接矩阵沿主对角线对称,即满足 (i, j) == (j, i)
this.adjMat[i][j] = 1;
this.adjMat[j][i] = 1;
}
/* 删除边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
removeEdge(i, j) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= this.size() || j >= this.size() || i === j) {
throw new RangeError("Index Out Of Bounds Exception");
}
this.adjMat[i][j] = 0;
this.adjMat[j][i] = 0;
}
/* 打印邻接矩阵 */
print() {
console.log("顶点列表 = ", this.vertices);
console.log("邻接矩阵 =", this.adjMat);
}
}
graph_adjacency_matrix.ts
/* 基于邻接矩阵实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjMat {
vertices: number[]; // 顶点列表,元素代表“顶点值”,索引代表“顶点索引”
adjMat: number[][]; // 邻接矩阵,行列索引对应“顶点索引”
/* 构造函数 */
constructor(vertices: number[], edges: number[][]) {
this.vertices = [];
this.adjMat = [];
// 添加顶点
for (const val of vertices) {
this.addVertex(val);
}
// 添加边
// 请注意,edges 元素代表顶点索引,即对应 vertices 元素索引
for (const e of edges) {
this.addEdge(e[0], e[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
size(): number {
return this.vertices.length;
}
/* 添加顶点 */
addVertex(val: number): void {
const n: number = this.size();
// 向顶点列表中添加新顶点的值
this.vertices.push(val);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一行
const newRow: number[] = [];
for (let j: number = 0; j < n; j++) {
newRow.push(0);
}
this.adjMat.push(newRow);
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一列
for (const row of this.adjMat) {
row.push(0);
}
}
/* 删除顶点 */
removeVertex(index: number): void {
if (index >= this.size()) {
throw new RangeError("Index Out Of Bounds Exception");
}
// 在顶点列表中移除索引 index 的顶点
this.vertices.splice(index, 1);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的行
this.adjMat.splice(index, 1);
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的列
for (const row of this.adjMat) {
row.splice(index, 1);
}
}
/* 添加边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
addEdge(i: number, j: number): void {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= this.size() || j >= this.size() || i === j) {
throw new RangeError("Index Out Of Bounds Exception");
}
// 在无向图中,邻接矩阵沿主对角线对称,即满足 (i, j) == (j, i)
this.adjMat[i][j] = 1;
this.adjMat[j][i] = 1;
}
/* 删除边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
removeEdge(i: number, j: number): void {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= this.size() || j >= this.size() || i === j) {
throw new RangeError("Index Out Of Bounds Exception");
}
this.adjMat[i][j] = 0;
this.adjMat[j][i] = 0;
}
/* 打印邻接矩阵 */
print(): void {
console.log("顶点列表 = ", this.vertices);
console.log("邻接矩阵 =", this.adjMat);
}
}
graph_adjacency_matrix.swift
/* 基于邻接矩阵实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjMat {
private var vertices: [Int] // 顶点列表,元素代表“顶点值”,索引代表“顶点索引”
private var adjMat: [[Int]] // 邻接矩阵,行列索引对应“顶点索引”
/* 构造方法 */
init(vertices: [Int], edges: [[Int]]) {
self.vertices = []
adjMat = []
// 添加顶点
for val in vertices {
addVertex(val: val)
}
// 添加边
// 请注意,edges 元素代表顶点索引,即对应 vertices 元素索引
for e in edges {
addEdge(i: e[0], j: e[1])
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
func size() -> Int {
vertices.count
}
/* 添加顶点 */
func addVertex(val: Int) {
let n = size()
// 向顶点列表中添加新顶点的值
vertices.append(val)
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一行
let newRow = Array(repeating: 0, count: n)
adjMat.append(newRow)
// 在邻接矩阵中添加一列
for i in adjMat.indices {
adjMat[i].append(0)
}
}
/* 删除顶点 */
func removeVertex(index: Int) {
if index >= size() {
fatalError("越界")
}
// 在顶点列表中移除索引 index 的顶点
vertices.remove(at: index)
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的行
adjMat.remove(at: index)
// 在邻接矩阵中删除索引 index 的列
for i in adjMat.indices {
adjMat[i].remove(at: index)
}
}
/* 添加边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
func addEdge(i: Int, j: Int) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= size() || j >= size() || i == j {
fatalError("越界")
}
// 在无向图中,邻接矩阵沿主对角线对称,即满足 (i, j) == (j, i)
adjMat[i][j] = 1
adjMat[j][i] = 1
}
/* 删除边 */
// 参数 i, j 对应 vertices 元素索引
func removeEdge(i: Int, j: Int) {
// 索引越界与相等处理
if i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= size() || j >= size() || i == j {
fatalError("越界")
}
adjMat[i][j] = 0
adjMat[j][i] = 0
}
/* 打印邻接矩阵 */
func print() {
Swift.print("顶点列表 = ", terminator: "")
Swift.print(vertices)
Swift.print("邻接矩阵 =")
PrintUtil.printMatrix(matrix: adjMat)
}
}
9.2.2. 基于邻接表的实现¶
设图的顶点总数为 \(n\) 、边总数为 \(m\) ,则有:
- 添加边:在顶点对应链表的尾部添加边即可,使用 \(O(1)\) 时间。因为是无向图,所以需要同时添加两个方向的边。
- 删除边:在顶点对应链表中查询与删除指定边,使用 \(O(m)\) 时间。与添加边一样,需要同时删除两个方向的边。
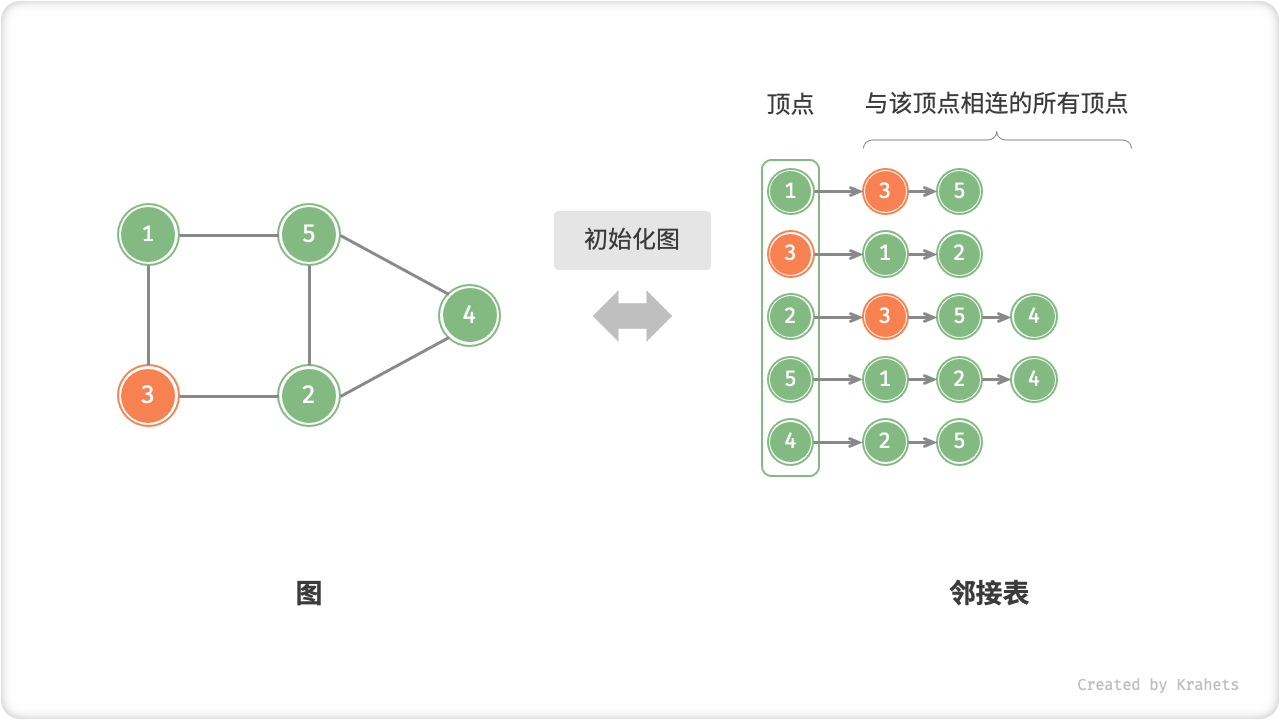
- 添加顶点:在邻接表中添加一个链表即可,并以新增顶点为链表头结点,使用 \(O(1)\) 时间。
- 删除顶点:需要遍历整个邻接表,删除包含指定顶点的所有边,使用 \(O(n + m)\) 时间。
- 初始化:需要在邻接表中建立 \(n\) 个结点和 \(2m\) 条边,使用 \(O(n + m)\) 时间。




基于邻接表实现图的代码如下所示。
为什么需要使用顶点类 Vertex ?
如果我们直接通过顶点值来区分不同顶点,那么值重复的顶点将无法被区分。
如果建立一个顶点列表,用索引来区分不同顶点,那么假设我们想要删除索引为 i 的顶点,则需要遍历整个邻接表,将其中 \(> i\) 的索引全部执行 \(-1\) ,这样的操作是比较耗时的。
因此,通过引入顶点类 Vertex ,每个顶点都是唯一的对象,这样在删除操作时就无需改动其余顶点了。
graph_adjacency_list.java
/* 基于邻接表实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjList {
// 邻接表,使用哈希表来代替链表,以提升删除边、删除顶点的效率
// 请注意,adjList 中的元素是 Vertex 对象
Map<Vertex, List<Vertex>> adjList;
/* 构造方法 */
public GraphAdjList(Vertex[][] edges) {
this.adjList = new HashMap<>();
// 添加所有顶点和边
for (Vertex[] edge : edges) {
addVertex(edge[0]);
addVertex(edge[1]);
addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
public int size() {
return adjList.size();
}
/* 添加边 */
public void addEdge(Vertex vet1, Vertex vet2) {
if (!adjList.containsKey(vet1) || !adjList.containsKey(vet2) || vet1 == vet2)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 添加边 vet1 - vet2
adjList.get(vet1).add(vet2);
adjList.get(vet2).add(vet1);
}
/* 删除边 */
public void removeEdge(Vertex vet1, Vertex vet2) {
if (!adjList.containsKey(vet1) || !adjList.containsKey(vet2) || vet1 == vet2)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 删除边 vet1 - vet2
adjList.get(vet1).remove(vet2);
adjList.get(vet2).remove(vet1);
}
/* 添加顶点 */
public void addVertex(Vertex vet) {
if (adjList.containsKey(vet))
return;
// 在邻接表中添加一个新链表
adjList.put(vet, new ArrayList<>());
}
/* 删除顶点 */
public void removeVertex(Vertex vet) {
if (!adjList.containsKey(vet))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 在邻接表中删除顶点 vet 对应的链表
adjList.remove(vet);
// 遍历其它顶点的链表,删除所有包含 vet 的边
for (List<Vertex> list : adjList.values()) {
list.remove(vet);
}
}
/* 打印邻接表 */
public void print() {
System.out.println("邻接表 =");
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, List<Vertex>> entry : adjList.entrySet()) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for (Vertex vertex : entry.getValue())
tmp.add(vertex.val);
System.out.println(entry.getKey().val + ": " + tmp + ",");
}
}
}
graph_adjacency_list.cpp
/* 基于邻接表实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjList {
// 邻接表,使用哈希表来代替链表,以提升删除边、删除顶点的效率
// 请注意,adjList 中的元素是 Vertex 对象
unordered_map<Vertex*, unordered_set<Vertex*>> adjList;
public:
/* 构造方法 */
GraphAdjList(const vector<vector<Vertex*>>& edges) {
// 添加所有顶点和边
for (const vector<Vertex*>& edge : edges) {
addVertex(edge[0]);
addVertex(edge[1]);
addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
int size() { return adjList.size(); }
/* 添加边 */
void addEdge(Vertex* vet1, Vertex* vet2) {
if (!adjList.count(vet1) || !adjList.count(vet2) || vet1 == vet2)
throw invalid_argument("不存在顶点");
// 添加边 vet1 - vet2
adjList[vet1].insert(vet2);
adjList[vet2].insert(vet1);
}
/* 删除边 */
void removeEdge(Vertex* vet1, Vertex* vet2) {
if (!adjList.count(vet1) || !adjList.count(vet2) || vet1 == vet2)
throw invalid_argument("不存在顶点");
// 删除边 vet1 - vet2
adjList[vet1].erase(vet2);
adjList[vet2].erase(vet1);
}
/* 添加顶点 */
void addVertex(Vertex* vet) {
if (adjList.count(vet)) return;
// 在邻接表中添加一个新链表
adjList[vet] = unordered_set<Vertex*>();
}
/* 删除顶点 */
void removeVertex(Vertex* vet) {
if (!adjList.count(vet))
throw invalid_argument("不存在顶点");
// 在邻接表中删除顶点 vet 对应的链表
adjList.erase(vet);
// 遍历其它顶点的链表,删除所有包含 vet 的边
for (auto& [key, set_] : adjList) {
set_.erase(vet);
}
}
/* 打印邻接表 */
void print() {
cout << "邻接表 =" << endl;
for (auto& [key, value] : adjList) {
vector<int> tmp;
for (Vertex* vertex : value)
tmp.push_back(vertex->val);
cout << key->val << ": ";
PrintUtil::printVector(tmp);
}
}
};
graph_adjacency_list.go
/* 基于邻接表实现的无向图类 */
type graphAdjList struct {
// 邻接表,使用哈希表来代替链表,以提升删除边、删除顶点的效率
// 请注意,adjList 中的元素是 Vertex 对象
adjList map[vertex]map[vertex]struct{}
}
/* 构造方法 */
func newGraphAdjList(edges [][]vertex) *graphAdjList {
g := &graphAdjList{
adjList: make(map[vertex]map[vertex]struct{}),
}
// 添加所有顶点和边
for _, edge := range edges {
g.addVertex(edge[0])
g.addVertex(edge[1])
g.addEdge(edge[0], edge[1])
}
return g
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
func (g *graphAdjList) size() int {
return len(g.adjList)
}
/* 添加边 */
func (g *graphAdjList) addEdge(vet1 vertex, vet2 vertex) {
_, ok1 := g.adjList[vet1]
_, ok2 := g.adjList[vet2]
if !ok1 || !ok2 || vet1 == vet2 {
panic("error")
}
// 添加边 vet1 - vet2, 添加匿名 struct{},
g.adjList[vet1][vet2] = struct{}{}
g.adjList[vet2][vet1] = struct{}{}
}
/* 删除边 */
func (g *graphAdjList) removeEdge(vet1 vertex, vet2 vertex) {
_, ok1 := g.adjList[vet1]
_, ok2 := g.adjList[vet2]
if !ok1 || !ok2 || vet1 == vet2 {
panic("error")
}
// 删除边 vet1 - vet2, 借助 delete 来删除 map 中的键
delete(g.adjList[vet1], vet2)
delete(g.adjList[vet2], vet1)
}
/* 添加顶点 */
func (g *graphAdjList) addVertex(vet vertex) {
_, ok := g.adjList[vet]
if ok {
return
}
// 在邻接表中添加一个新链表
g.adjList[vet] = make(map[vertex]struct{})
}
/* 删除顶点 */
func (g *graphAdjList) removeVertex(vet vertex) {
_, ok := g.adjList[vet]
if !ok {
panic("error")
}
// 在邻接表中删除顶点 vet 对应的链表
delete(g.adjList, vet)
// 遍历其它顶点的链表,删除所有包含 vet 的边
for _, set := range g.adjList {
// 操作
delete(set, vet)
}
}
/* 打印邻接表 */
func (g *graphAdjList) print() {
var builder strings.Builder
fmt.Printf("邻接表 = \n")
for k, v := range g.adjList {
builder.WriteString("\t\t" + strconv.Itoa(k.val) + ": ")
for vet := range v {
builder.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(vet.val) + " ")
}
fmt.Println(builder.String())
builder.Reset()
}
}
graph_adjacency_list.js
/* 基于邻接表实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjList {
// 邻接表,使用哈希表来代替链表,以提升删除边、删除顶点的效率
// 请注意,adjList 中的元素是 Vertex 对象
adjList;
/* 构造方法 */
constructor(edges) {
this.adjList = new Map();
// 添加所有顶点和边
for (const edge of edges) {
this.addVertex(edge[0]);
this.addVertex(edge[1]);
this.addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
size() {
return this.adjList.size;
}
/* 添加边 */
addEdge(vet1, vet2) {
if (!this.adjList.has(vet1) || !this.adjList.has(vet2) || vet1 === vet2) {
throw new Error("Illegal Argument Exception");
}
// 添加边 vet1 - vet2
this.adjList.get(vet1).add(vet2);
this.adjList.get(vet2).add(vet1);
}
/* 删除边 */
removeEdge(vet1, vet2) {
if (!this.adjList.has(vet1) || !this.adjList.has(vet2) || vet1 === vet2) {
throw new Error("Illegal Argument Exception");
}
// 删除边 vet1 - vet2
this.adjList.get(vet1).delete(vet2);
this.adjList.get(vet2).delete(vet1);
}
/* 添加顶点 */
addVertex(vet) {
if (this.adjList.has(vet)) return;
// 在邻接表中添加一个新链表
this.adjList.set(vet, new Set());
}
/* 删除顶点 */
removeVertex(vet) {
if (!this.adjList.has(vet)) {
throw new Error("Illegal Argument Exception");
}
// 在邻接表中删除顶点 vet 对应的链表
this.adjList.delete(vet);
// 遍历其它顶点的链表,删除所有包含 vet 的边
for (let set of this.adjList.values()) {
set.delete(vet);
}
}
/* 打印邻接表 */
print() {
console.log("邻接表 =");
for (const [key, value] of this.adjList) {
const tmp = [];
for (const vertex of value){
tmp.push(vertex.val);
}
console.log(key.val + ": " + tmp + ",");
}
}
}
graph_adjacency_list.ts
/* 基于邻接表实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjList {
// 邻接表,使用哈希表来代替链表,以提升删除边、删除顶点的效率
// 请注意,adjList 中的元素是 Vertex 对象
adjList: Map<Vertex, Set<Vertex>>;
/* 构造方法 */
constructor(edges: Vertex[][]) {
this.adjList = new Map();
// 添加所有顶点和边
for (const edge of edges) {
this.addVertex(edge[0]);
this.addVertex(edge[1]);
this.addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
size(): number {
return this.adjList.size;
}
/* 添加边 */
addEdge(vet1: Vertex, vet2: Vertex): void {
if (!this.adjList.has(vet1) || !this.adjList.has(vet2) || vet1 === vet2) {
throw new Error("Illegal Argument Exception");
}
// 添加边 vet1 - vet2
this.adjList.get(vet1).add(vet2);
this.adjList.get(vet2).add(vet1);
}
/* 删除边 */
removeEdge(vet1: Vertex, vet2: Vertex): void {
if (!this.adjList.has(vet1) || !this.adjList.has(vet2) || vet1 === vet2) {
throw new Error("Illegal Argument Exception");
}
// 删除边 vet1 - vet2
this.adjList.get(vet1).delete(vet2);
this.adjList.get(vet2).delete(vet1);
}
/* 添加顶点 */
addVertex(vet: Vertex): void {
if (this.adjList.has(vet)) return;
// 在邻接表中添加一个新链表
this.adjList.set(vet, new Set());
}
/* 删除顶点 */
removeVertex(vet: Vertex): void {
if (!this.adjList.has(vet)) {
throw new Error("Illegal Argument Exception");
}
// 在邻接表中删除顶点 vet 对应的链表
this.adjList.delete(vet);
// 遍历其它顶点的链表,删除所有包含 vet 的边
for (let set of this.adjList.values()) {
set.delete(vet);
}
}
/* 打印邻接表 */
print(): void {
console.log("邻接表 =");
for (const [key, value] of this.adjList.entries()) {
const tmp = [];
for (const vertex of value){
tmp.push(vertex.val);
}
console.log(key.val + ": " + tmp + ",");
}
}
}
graph_adjacency_list.swift
/* 基于邻接表实现的无向图类 */
class GraphAdjList {
// 邻接表,使用哈希表来代替链表,以提升删除边、删除顶点的效率
// 请注意,adjList 中的元素是 Vertex 对象
private var adjList: [Vertex: Set<Vertex>]
/* 构造方法 */
init(edges: [[Vertex]]) {
adjList = [:]
// 添加所有顶点和边
for edge in edges {
addVertex(vet: edge[0])
addVertex(vet: edge[1])
addEdge(vet1: edge[0], vet2: edge[1])
}
}
/* 获取顶点数量 */
func size() -> Int {
adjList.count
}
/* 添加边 */
func addEdge(vet1: Vertex, vet2: Vertex) {
if adjList[vet1] == nil || adjList[vet2] == nil || vet1 == vet2 {
fatalError("参数错误")
}
// 添加边 vet1 - vet2
adjList[vet1]?.insert(vet2)
adjList[vet2]?.insert(vet1)
}
/* 删除边 */
func removeEdge(vet1: Vertex, vet2: Vertex) {
if adjList[vet1] == nil || adjList[vet2] == nil || vet1 == vet2 {
fatalError("参数错误")
}
// 删除边 vet1 - vet2
adjList[vet1]?.remove(vet2)
adjList[vet2]?.remove(vet1)
}
/* 添加顶点 */
func addVertex(vet: Vertex) {
if adjList[vet] != nil {
return
}
// 在邻接表中添加一个新链表
adjList[vet] = []
}
/* 删除顶点 */
func removeVertex(vet: Vertex) {
if adjList[vet] == nil {
fatalError("参数错误")
}
// 在邻接表中删除顶点 vet 对应的链表
adjList.removeValue(forKey: vet)
// 遍历其它顶点的链表,删除所有包含 vet 的边
for key in adjList.keys {
adjList[key]?.remove(vet)
}
}
/* 打印邻接表 */
func print() {
Swift.print("邻接表 =")
for entry in adjList {
var tmp: [Int] = []
for vertex in entry.value {
tmp.append(vertex.val)
}
Swift.print("\(entry.key.val): \(tmp),")
}
}
}
9.2.3. 效率对比¶
设图中共有 \(n\) 个顶点和 \(m\) 条边,下表为邻接矩阵和邻接表的时间和空间效率对比。
| 邻接矩阵 | 邻接表(链表) | 邻接表(哈希表) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 判断是否邻接 | \(O(1)\) | \(O(m)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| 添加边 | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| 删除边 | \(O(1)\) | \(O(m)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| 添加顶点 | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| 删除顶点 | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n + m)\) | \(O(n)\) |
| 内存空间占用 | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n + m)\) | \(O(n + m)\) |
观察上表,貌似邻接表(哈希表)的时间与空间效率最优。但实际上,在邻接矩阵中操作边的效率更高,只需要一次数组访问或赋值操作即可。总结以上,邻接矩阵体现“以空间换时间”,邻接表体现“以时间换空间”。