20 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
队列
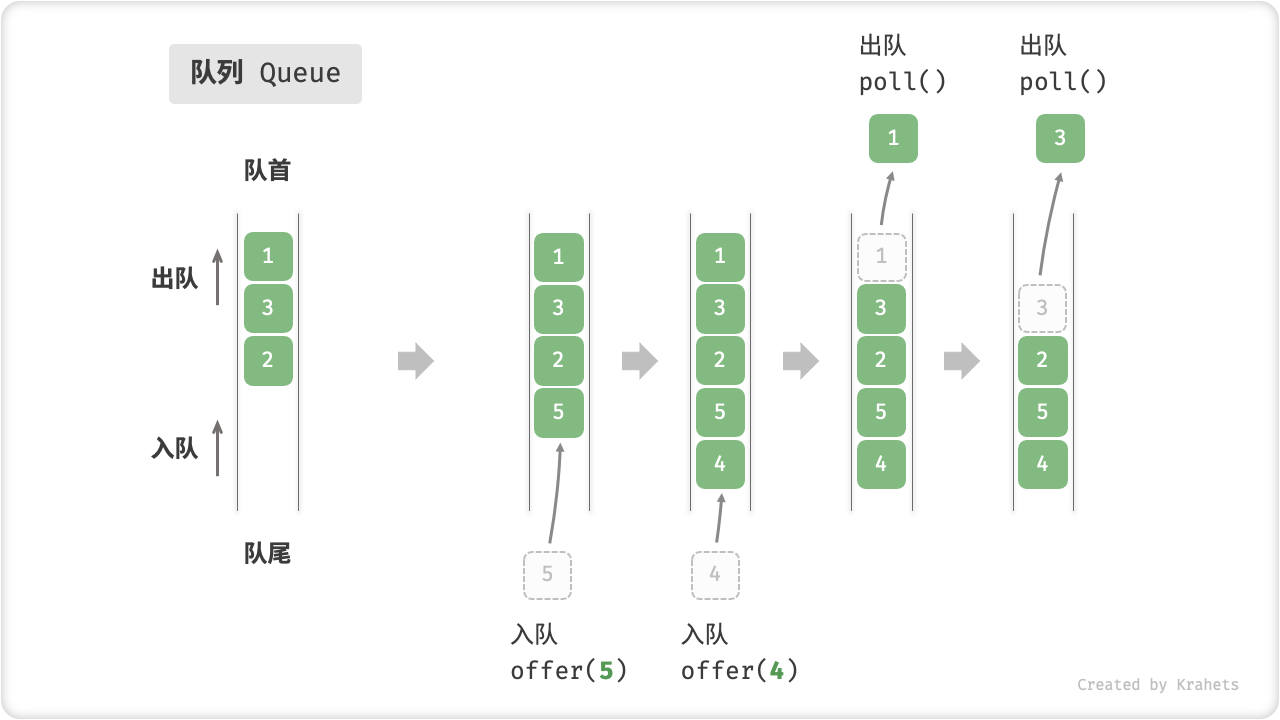
「队列 Queue」是一种遵循「先入先出 first in, first out」数据操作规则的线性数据结构。顾名思义,队列模拟的是排队现象,即外面的人不断加入队列尾部,而处于队列头部的人不断地离开。
我们将队列头部称为「队首」,队列尾部称为「队尾」,将把元素加入队尾的操作称为「入队」,删除队首元素的操作称为「出队」。
Fig. 队列的先入先出特性
队列常用操作
队列的常用操作见下表,方法命名需根据编程语言的设定来具体确定。
Table. 队列的常用操作
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| offer() | 元素入队,即将元素添加至队尾 |
| poll() | 队首元素出队 |
| front() | 访问队首元素 |
| size() | 获取队列的长度 |
| isEmpty() | 判断队列是否为空 |
我们可以直接使用编程语言实现好的队列类。
=== "Java"
```java title="queue.java"
/* 初始化队列 */
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
/* 元素入队 */
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(5);
queue.offer(4);
/* 访问队首元素 */
int peek = queue.peek();
/* 元素出队 */
int poll = queue.poll();
/* 获取队列的长度 */
int size = queue.size();
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
boolean isEmpty = queue.isEmpty();
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="queue.cpp"
/* 初始化队列 */
queue<int> queue;
/* 元素入队 */
queue.push(1);
queue.push(3);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(5);
queue.push(4);
/* 访问队首元素 */
int front = queue.front();
/* 元素出队 */
queue.pop();
/* 获取队列的长度 */
int size = queue.size();
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
bool empty = queue.empty();
```
=== "Python"
```python title="queue.py"
""" 初始化队列 """
# 在 Python 中,我们一般将双向队列类 deque 看左队列使用
# 虽然 queue.Queue() 是纯正的队列类,但不太好用,因此不建议
que = collections.deque()
""" 元素入队 """
que.append(1)
que.append(3)
que.append(2)
que.append(5)
que.append(4)
""" 访问队首元素 """
front = que[0];
""" 元素出队 """
pop = que.popleft()
""" 获取队列的长度 """
size = len(que)
""" 判断队列是否为空 """
is_empty = len(que) == 0
```
=== "Go"
```go title="queue.go"
/* 初始化队列 */
// 在 Go 中,将 list 作为队列来使用
queue := list.New()
/* 元素入队 */
queue.PushBack(1)
queue.PushBack(3)
queue.PushBack(2)
queue.PushBack(5)
queue.PushBack(4)
/* 访问队首元素 */
peek := queue.Front()
/* 元素出队 */
poll := queue.Front()
queue.Remove(poll)
/* 获取队列的长度 */
size := queue.Len()
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
isEmpty := queue.Len() == 0
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="queue.js"
/* 初始化队列 */
// Javascript 没有内置的队列,可以把 Array 当作队列来使用
// 注意:虽然Javascript有shift()函数可以去除队首元素,但是时间复杂度是O(n)的。
const queue = [];
/* 元素入队 */
queue.push(1);
queue.push(3);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(5);
queue.push(4);
/* 访问队首元素 */
const peek = queue[0];
/* 元素出队 */
const poll = queue.shift();
/* 获取队列的长度 */
const size = queue.length;
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
const empty = queue.length === 0;
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="queue.ts"
/* 初始化队列 */
// Typescript 没有内置的队列,可以把 Array 当作队列来使用
// 注意:虽然Typescript有shift()函数可以去除队首元素,但是时间复杂度是O(n)的。
const queue: number[] = [];
/* 元素入队 */
queue.push(1);
queue.push(3);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(5);
queue.push(4);
/* 访问队首元素 */
const peek = queue[0];
/* 元素出队 */
const poll = queue.shift();
/* 获取队列的长度 */
const size = queue.length;
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
const empty = queue.length === 0;
```
=== "C"
```c title="queue.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="queue.cs"
```
队列实现
队列需要一种可以在一端添加,并在另一端删除的数据结构,也可以使用链表或数组来实现。
基于链表的实现
我们将链表的「头结点」和「尾结点」分别看作是队首和队尾,并规定队尾只可添加结点,队首只可删除结点。
=== "Java"
```java title="linkedlist_queue.java"
/* 基于链表实现的队列 */
class LinkedListQueue {
private ListNode front, rear; // 头结点 front ,尾结点 rear
private int queSize = 0;
public LinkedListQueue() {
front = null;
rear = null;
}
/* 获取队列的长度 */
public int size() {
return queSize;
}
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/* 入队 */
public void offer(int num) {
// 尾结点后添加 num
ListNode node = new ListNode(num);
// 如果队列为空,则令头、尾结点都指向该结点
if (front == null) {
front = node;
rear = node;
// 如果队列不为空,则将该结点添加到尾结点后
} else {
rear.next = node;
rear = node;
}
queSize++;
}
/* 出队 */
public int poll() {
int num = peek();
// 删除头结点
front = front.next;
queSize--;
return num;
}
/* 访问队首元素 */
public int peek() {
if (size() == 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return front.val;
}
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="linkedlist_queue.cpp"
/* 基于链表实现的队列 */
class LinkedListQueue {
private:
ListNode *front, *rear; // 头结点 front ,尾结点 rear
int queSize;
public:
LinkedListQueue() {
front = nullptr;
rear = nullptr;
queSize = 0;
}
/* 获取队列的长度 */
int size() {
return queSize;
}
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
bool empty() {
return queSize == 0;
}
/* 入队 */
void offer(int num) {
// 尾结点后添加 num
ListNode* node = new ListNode(num);
// 如果队列为空,则令头、尾结点都指向该结点
if (front == nullptr) {
front = node;
rear = node;
}
// 如果队列不为空,则将该结点添加到尾结点后
else {
rear->next = node;
rear = node;
}
queSize++;
}
/* 出队 */
int poll() {
int num = peek();
// 删除头结点
front = front->next;
queSize--;
return num;
}
/* 访问队首元素 */
int peek() {
if (size() == 0)
throw out_of_range("队列为空");
return front->val;
}
};
```
=== "Python"
```python title="linkedlist_queue.py"
""" 基于链表实现的队列 """
class LinkedListQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.__front = None # 头结点 front
self.__rear = None # 尾结点 rear
self.__size = 0
""" 获取队列的长度 """
def size(self):
return self.__size
""" 判断队列是否为空 """
def is_empty(self):
return not self.__front
""" 入队 """
def push(self, num):
# 尾结点后添加 num
node = ListNode(num)
# 如果队列为空,则令头、尾结点都指向该结点
if self.__front == 0:
self.__front = node
self.__rear = node
# 如果队列不为空,则将该结点添加到尾结点后
else:
self.__rear.next = node
self.__rear = node
self.__size += 1
""" 出队 """
def poll(self):
num = self.peek()
# 删除头结点
self.__front = self.__front.next
self.__size -= 1
return num
""" 访问队首元素 """
def peek(self):
if self.size() == 0:
print("队列为空")
return False
return self.__front.val
```
=== "Go"
```go title="linkedlist_queue.go"
/* 基于链表实现的队列 */
type LinkedListQueue struct {
// 使用内置包 list 来实现队列
data *list.List
}
// NewLinkedListQueue 初始化链表
func NewLinkedListQueue() *LinkedListQueue {
return &LinkedListQueue{
data: list.New(),
}
}
// Offer 入队
func (s *LinkedListQueue) Offer(value any) {
s.data.PushBack(value)
}
// Poll 出队
func (s *LinkedListQueue) Poll() any {
if s.IsEmpty() {
return nil
}
e := s.data.Front()
s.data.Remove(e)
return e.Value
}
// Peek 访问队首元素
func (s *LinkedListQueue) Peek() any {
if s.IsEmpty() {
return nil
}
e := s.data.Front()
return e.Value
}
// Size 获取队列的长度
func (s *LinkedListQueue) Size() int {
return s.data.Len()
}
// IsEmpty 判断队列是否为空
func (s *LinkedListQueue) IsEmpty() bool {
return s.data.Len() == 0
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="linkedlist_queue.js"
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="linkedlist_queue.ts"
```
=== "C"
```c title="linkedlist_queue.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="linkedlist_queue.cs"
```
基于数组的实现
数组的删除首元素的时间复杂度为 O(n) ,因此不适合直接用来实现队列。然而,我们可以借助两个指针 front , rear 来分别记录队首和队尾的索引位置,在入队 / 出队时分别将 front / rear 向后移动一位即可,这样每次仅需操作一个元素,时间复杂度降至 O(1) 。
还有一个问题,在入队与出队的过程中,两个指针都在向后移动,而到达尾部后则无法继续移动了。为了解决此问题,我们可以采取一个取巧方案,即将数组看作是 “环形” 的。具体做法是规定指针越过数组尾部后,再次回到头部接续遍历,这样相当于使数组 “首尾相连” 了。
为了适应环形数组的设定,获取长度 size() 、入队 offer() 、出队 poll() 方法都需要做相应的取余操作处理,使得当尾指针绕回数组头部时,仍然可以正确处理操作。
基于数组实现的队列有一个缺点,即长度不可变。但这点我们可以通过动态数组来解决,有兴趣的同学可以自行实现。
=== "Java"
```java title="array_queue.java"
/* 基于环形数组实现的队列 */
class ArrayQueue {
private int[] nums; // 用于存储队列元素的数组
private int front = 0; // 头指针,指向队首
private int rear = 0; // 尾指针,指向队尾 + 1
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
// 初始化数组
nums = new int[capacity];
}
/* 获取队列的容量 */
public int capacity() {
return nums.length;
}
/* 获取队列的长度 */
public int size() {
int capacity = capacity();
// 由于将数组看作为环形,可能 rear < front ,因此需要取余数
return (capacity + rear - front) % capacity;
}
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear - front == 0;
}
/* 入队 */
public void offer(int num) {
if (size() == capacity()) {
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
// 尾结点后添加 num
nums[rear] = num;
// 尾指针向后移动一位,越过尾部后返回到数组头部
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity();
}
/* 出队 */
public int poll() {
int num = peek();
// 队头指针向后移动一位,若越过尾部则返回到数组头部
front = (front + 1) % capacity();
return num;
}
/* 访问队首元素 */
public int peek() {
// 删除头结点
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyStackException();
return nums[front];
}
/* 访问指定索引元素 */
int get(int index) {
if (index >= size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return nums[(front + index) % capacity()];
}
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="array_queue.cpp"
/* 基于环形数组实现的队列 */
class ArrayQueue {
private:
int *nums; // 用于存储队列元素的数组
int cap; // 队列容量
int front = 0; // 头指针,指向队首
int rear = 0; // 尾指针,指向队尾 + 1
public:
ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
// 初始化数组
cap = capacity;
nums = new int[capacity];
}
/* 获取队列的容量 */
int capacity() {
return cap;
}
/* 获取队列的长度 */
int size() {
// 由于将数组看作为环形,可能 rear < front ,因此需要取余数
return (capacity() + rear - front) % capacity();
}
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
bool empty() {
return rear - front == 0;
}
/* 入队 */
void offer(int num) {
if (size() == capacity()) {
cout << "队列已满" << endl;
return;
}
// 尾结点后添加 num
nums[rear] = num;
// 尾指针向后移动一位,越过尾部后返回到数组头部
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity();
}
/* 出队 */
int poll() {
int num = peek();
// 队头指针向后移动一位,若越过尾部则返回到数组头部
front = (front + 1) % capacity();
return num;
}
/* 访问队首元素 */
int peek() {
// 删除头结点
if (empty())
throw out_of_range("队列为空");
return nums[front];
}
/* 访问指定位置元素 */
int get(int index) {
if (index >= size())
throw out_of_range("索引越界");
return nums[(front + index) % capacity()]
}
};
```
=== "Python"
```python title="array_queue.py"
""" 基于环形数组实现的队列 """
class ArrayQueue:
def __init__(self, size):
self.__nums = [0] * size # 用于存储队列元素的数组
self.__front = 0 # 头指针,指向队首
self.__rear = 0 # 尾指针,指向队尾 + 1
""" 获取队列的容量 """
def capacity(self):
return len(self.__nums)
""" 获取队列的长度 """
def size(self):
# 由于将数组看作为环形,可能 rear < front ,因此需要取余数
return (self.capacity() + self.__rear - self.__front) % self.capacity()
""" 判断队列是否为空 """
def is_empty(self):
return (self.__rear - self.__front) == 0
""" 入队 """
def push(self, val):
if self.size() == self.capacity():
print("队列已满")
return False
# 尾结点后添加 num
self.__nums[self.__rear] = val
# 尾指针向后移动一位,越过尾部后返回到数组头部
self.__rear = (self.__rear + 1) % self.capacity()
""" 出队 """
def poll(self):
# 删除头结点
num = self.peek()
# 队头指针向后移动一位,若越过尾部则返回到数组头部
self.__front = (self.__front + 1) % self.capacity()
return num
""" 访问队首元素 """
def peek(self):
# 删除头结点
if self.is_empty():
print("队列为空")
return False
return self.__nums[self.__front]
""" 访问指定位置元素 """
def get(self, index):
if index >= self.size():
print("索引越界")
return False
return self.__nums[(self.__front + index) % self.capacity()]
""" 返回列表用于打印 """
def to_list(self):
res = [0] * self.size()
j = self.__front
for i in range(self.size()):
res[i] = self.__nums[(j % self.capacity())]
j += 1
return res
```
=== "Go"
```go title="array_queue.go"
/* 基于环形数组实现的队列 */
type ArrayQueue struct {
data []int // 用于存储队列元素的数组
capacity int // 队列容量(即最多容量的元素个数)
front int // 头指针,指向队首
rear int // 尾指针,指向队尾 + 1
}
// NewArrayQueue 基于环形数组实现的队列
func NewArrayQueue(capacity int) *ArrayQueue {
return &ArrayQueue{
data: make([]int, capacity),
capacity: capacity,
front: 0,
rear: 0,
}
}
// Size 获取队列的长度
func (q *ArrayQueue) Size() int {
size := (q.capacity + q.rear - q.front) % q.capacity
return size
}
// IsEmpty 判断队列是否为空
func (q *ArrayQueue) IsEmpty() bool {
return q.rear-q.front == 0
}
// Offer 入队
func (q *ArrayQueue) Offer(v int) {
// 当 rear == capacity 表示队列已满
if q.Size() == q.capacity {
return
}
// 尾结点后添加
q.data[q.rear] = v
// 尾指针向后移动一位,越过尾部后返回到数组头部
q.rear = (q.rear + 1) % q.capacity
}
// Poll 出队
func (q *ArrayQueue) Poll() any {
if q.IsEmpty() {
return nil
}
v := q.data[q.front]
// 队头指针向后移动一位,若越过尾部则返回到数组头部
q.front = (q.front + 1) % q.capacity
return v
}
// Peek 访问队首元素
func (q *ArrayQueue) Peek() any {
if q.IsEmpty() {
return nil
}
v := q.data[q.front]
return v
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="array_queue.js"
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="array_queue.ts"
```
=== "C"
```c title="array_queue.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="array_queue.cs"
```
队列典型应用
- 淘宝订单。 购物者下单后,订单就被加入到队列之中,随后系统再根据顺序依次处理队列中的订单。在双十一时,在短时间内会产生海量的订单,如何处理「高并发」则是工程师们需要重点思考的问题。
- 各种待办事项。 例如打印机的任务队列、餐厅的出餐队列等等。