You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
7.5 KiB
7.5 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
10.3. 哈希查找
!!! question
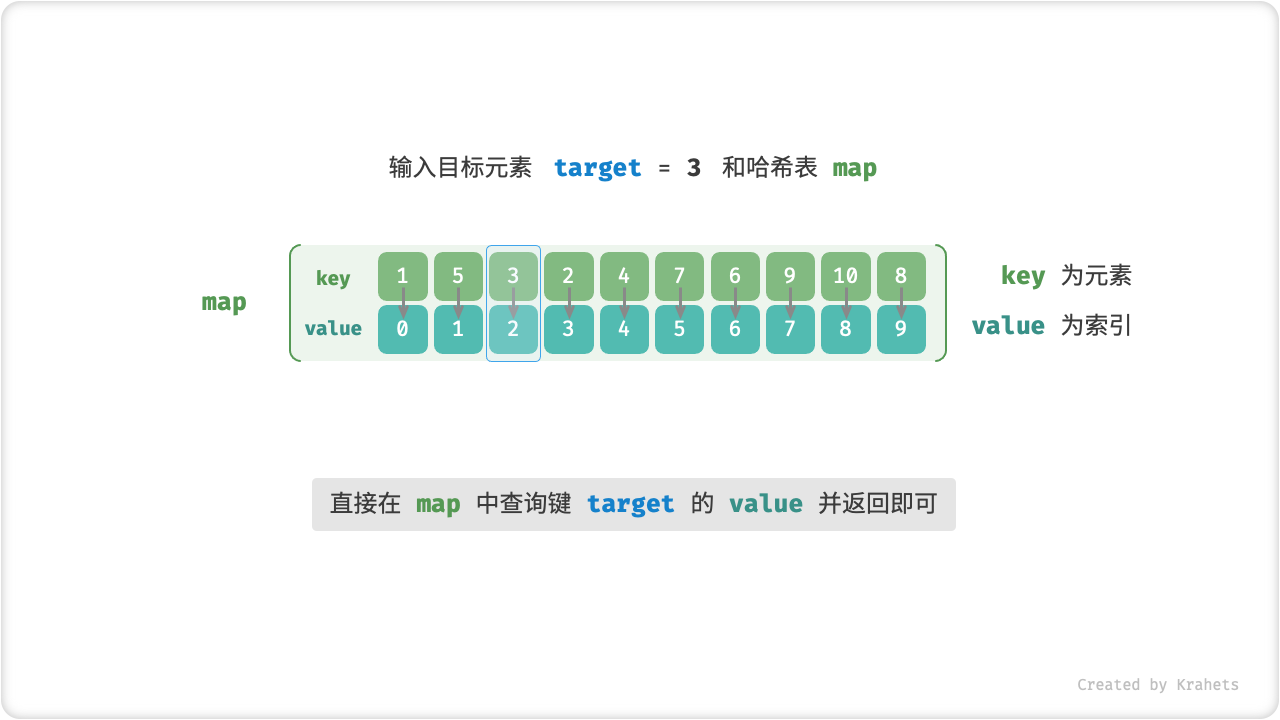
在数据量很大时,「线性查找」太慢;而「二分查找」要求数据必须是有序的,并且只能在数组中应用。那么是否有方法可以同时避免上述缺点呢?答案是肯定的,此方法被称为「哈希查找」。
「哈希查找 Hash Searching」借助一个哈希表来存储需要的「键值对 Key Value Pair」,我们可以在 O(1) 时间下实现“键 \rightarrow 值”映射查找,体现着“以空间换时间”的算法思想。
10.3.1. 算法实现
如果我们想要给定数组中的一个目标元素 target ,获取该元素的索引,那么可以借助一个哈希表实现查找。
=== "Java"
```java title="hashing_search.java"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
int hashingSearch(Map<Integer, Integer> map, int target) {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return map.getOrDefault(target, -1);
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="hashing_search.cpp"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
int hashingSearch(unordered_map<int, int> map, int target) {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
if (map.find(target) == map.end())
return -1;
return map[target];
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="hashing_search.py"
""" 哈希查找(数组) """
def hashing_search(mapp, target):
# 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
# 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return mapp.get(target, -1)
```
=== "Go"
```go title="hashing_search.go"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
func hashingSearch(m map[int]int, target int) int {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
if index, ok := m[target]; ok {
return index
} else {
return -1
}
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="hashing_search.js"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
function hashingSearch(map, target) {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return map.has(target) ? map.get(target) : -1;
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="hashing_search.ts"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
function hashingSearch(map: Map<number, number>, target: number): number {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return map.has(target) ? map.get(target) as number : -1;
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="hashing_search.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="hashing_search.cs"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
int hashingSearch(Dictionary<int, int> map, int target)
{
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return map.GetValueOrDefault(target, -1);
}
```
=== "Swift"
```swift title="hashing_search.swift"
/* 哈希查找(数组) */
func hashingSearch(map: [Int: Int], target: Int) -> Int {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 索引
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return map[target, default: -1]
}
```
=== "Zig"
```zig title="hashing_search.zig"
```
再比如,如果我们想要给定一个目标结点值 target ,获取对应的链表结点对象,那么也可以使用哈希查找实现。
=== "Java"
```java title="hashing_search.java"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
ListNode hashingSearch1(Map<Integer, ListNode> map, int target) {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 null
return map.getOrDefault(target, null);
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="hashing_search.cpp"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
ListNode* hashingSearch1(unordered_map<int, ListNode*> map, int target) {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 nullptr
if (map.find(target) == map.end())
return nullptr;
return map[target];
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="hashing_search.py"
""" 哈希查找(链表) """
def hashing_search1(mapp, target):
# 哈希表的 key: 目标元素,value: 结点对象
# 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 -1
return mapp.get(target, -1)
```
=== "Go"
```go title="hashing_search.go"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
func hashingSearch1(m map[int]*ListNode, target int) *ListNode {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 nil
if node, ok := m[target]; ok {
return node
} else {
return nil
}
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="hashing_search.js"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
function hashingSearch1(map, target) {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 null
return map.has(target) ? map.get(target) : null;
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="hashing_search.ts"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
function hashingSearch1(map: Map<number, ListNode>, target: number): ListNode | null {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 null
return map.has(target) ? map.get(target) as ListNode : null;
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="hashing_search.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="hashing_search.cs"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
ListNode? hashingSearch1(Dictionary<int, ListNode> map, int target)
{
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 null
return map.GetValueOrDefault(target);
}
```
=== "Swift"
```swift title="hashing_search.swift"
/* 哈希查找(链表) */
func hashingSearch1(map: [Int: ListNode], target: Int) -> ListNode? {
// 哈希表的 key: 目标结点值,value: 结点对象
// 若哈希表中无此 key ,返回 null
return map[target]
}
```
=== "Zig"
```zig title="hashing_search.zig"
```
10.3.2. 复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(1) :哈希表的查找操作使用 O(1) 时间。
空间复杂度 O(n) :其中 n 为数组或链表长度。
10.3.3. 优点与缺点
在哈希表中,查找、插入、删除操作的平均时间复杂度都为 O(1) ,这意味着无论是高频增删还是高频查找场景,哈希查找的性能表现都非常好。当然,一切的前提是保证哈希表未退化。
即使如此,哈希查找仍存在一些问题,在实际应用中,需要根据情况灵活选择方法。
- 辅助哈希表 需要使用
O(n)的额外空间,意味着需要预留更多的计算机内存; - 建立和维护哈希表需要时间,因此哈希查找 不适合高频增删、低频查找的使用场景;
- 当哈希冲突严重时,哈希表会退化为链表,时间复杂度劣化至
O(n); - 当数据量很小时,线性查找比哈希查找更快。这是因为计算哈希映射函数可能比遍历一个小型数组更慢;