5.8 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
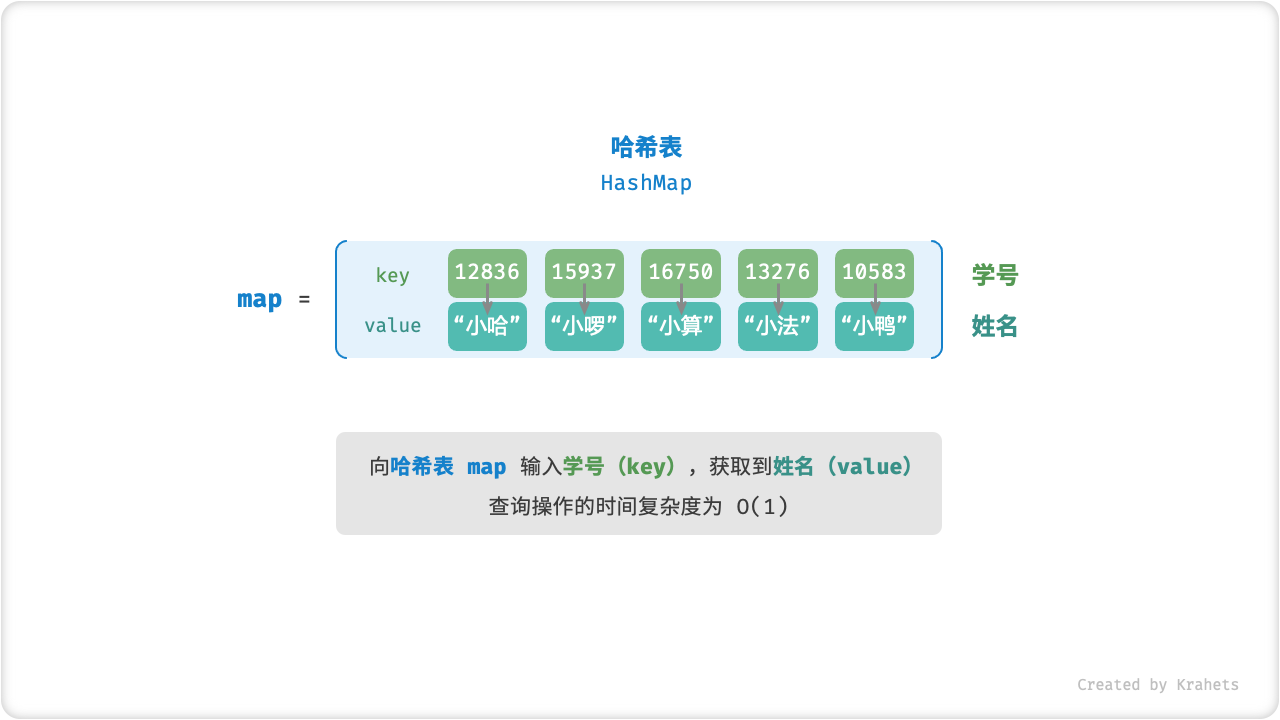
哈希表
哈希表通过建立「键 Key」和「值 Value」之间的映射,实现高效的元素查找。具体地,输入一个 Key ,在哈希表中查询并获取 Value ,时间复杂度为 O(1) 。
例如,给定一个包含 n 个学生的数据库,每个学生有 "姓名 name ” 和 “学号 id ” 两项数据,希望实现一个查询功能:输入一个学号,返回对应的姓名,则可以使用哈希表实现。
Fig. 哈希表抽象表示
哈希表优势
除了哈希表之外,还可以使用以下数据结构来实现上述查询功能:
- 无序数组: 每个元素为
[学号, 姓名]; - 有序数组: 将
1.中的数组按照学号从小到大排序; - 链表: 每个结点的值为
[学号, 姓名]; - 二叉搜索树: 每个结点的值为
[学号, 姓名],根据学号大小来构建树;
使用上述方法,各项操作的时间复杂度如下表所示(在此不做赘述,详解可见 二叉搜索树章节)。无论是查找元素、还是增删元素,哈希表的时间复杂度都是 O(1) ,全面胜出!
| 无序数组 | 有序数组 | 链表 | 二叉搜索树 | 哈希表 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 查找元素 | O(n) |
O(\log n) |
O(n) |
O(\log n) |
O(1) |
| 插入元素 | O(1) |
O(n) |
O(1) |
O(\log n) |
O(1) |
| 删除元素 | O(n) |
O(n) |
O(n) |
O(\log n) |
O(1) |
哈希表常用操作
哈希表的基本操作包括 初始化、查询操作、添加与删除键值对。
/* 初始化哈希表 */
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
/* 添加操作 */
// 在哈希表中添加键值对 (key, value)
map.put(12836, "小哈");
map.put(15937, "小啰");
map.put(16750, "小算");
map.put(13276, "小法");
map.put(10583, "小鸭");
/* 查询操作 */
// 向哈希表输入键 key ,得到值 value
String name = map.get(15937);
/* 删除操作 */
// 在哈希表中删除键值对 (key, value)
map.remove(10583);
遍历哈希表有三种方式,即 遍历键值对、遍历键、遍历值。
/* 遍历哈希表 */
// 遍历键值对 Key->Value
for (Map.Entry <Integer, String> kv: map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(kv.getKey() + " -> " + kv.getValue());
}
// 单独遍历键 Key
for (int key: map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
}
// 单独遍历值 Value
for (String val: map.values()) {
System.out.println(val);
}
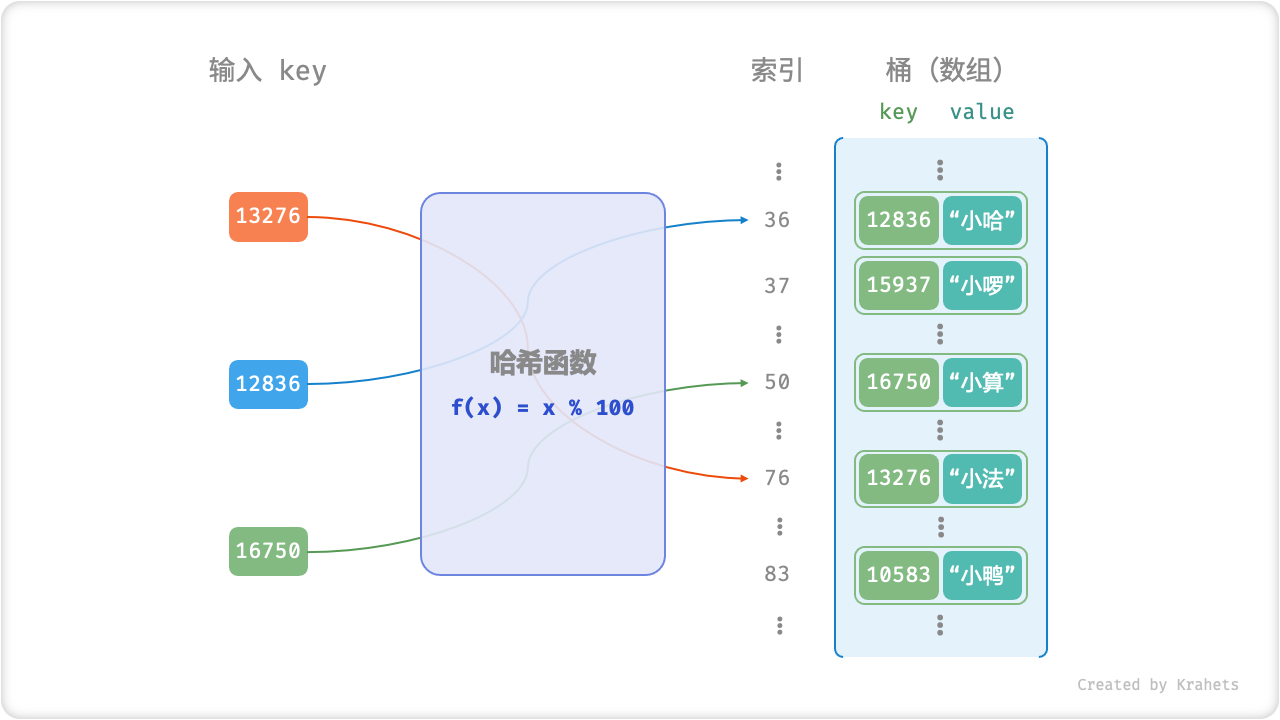
哈希函数
哈希表中存储元素的数据结构被称为「桶 Bucket」,底层实现可能是数组、链表、二叉树(红黑树),或是它们的组合。
最简单地,我们可以仅用一个「数组」来实现哈希表。首先,将所有 Value 放入数组中,那么每个 Value 在数组中都有唯一的「索引」。显然,访问 Value 需要给定索引,而为了 建立 Key 和索引之间的映射关系,我们需要使用「哈希函数 Hash Function」。
设数组为 bucket ,哈希函数为 f(x) ,输入键为 key 。那么获取 Value 的步骤为:
- 通过哈希函数计算出索引,即
index = f(key); - 通过索引在数组中获取值,即
value = bucket[index];
以上述学生数据 Key 学号 -> Value 姓名 为例,我们可以将「哈希函数」设计为
f(x) = x \% 100
Fig. 哈希函数
/* 键值对 int->String */
class Entry {
public int key; // 键
public String val; // 值
public Entry(int key, String val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
/* 基于数组简易实现的哈希表 */
class ArrayHashMap {
private List<Entry> bucket;
public ArrayHashMap() {
// 初始化一个长度为 100 的桶(数组)
bucket = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
bucket.add(null);
}
}
/* 哈希函数 */
private int hashFunc(int key) {
int index = key % 100;
return index;
}
/* 查询操作 */
public String get(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
Entry pair = bucket.get(index);
if (pair == null) return null;
return pair.val;
}
/* 添加操作 */
public void put(int key, String val) {
Entry pair = new Entry(key, val);
int index = hashFunc(key);
bucket.set(index, pair);
}
/* 删除操作 */
public void remove(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
// 置为空字符,代表删除
bucket.set(index, null);
}
}
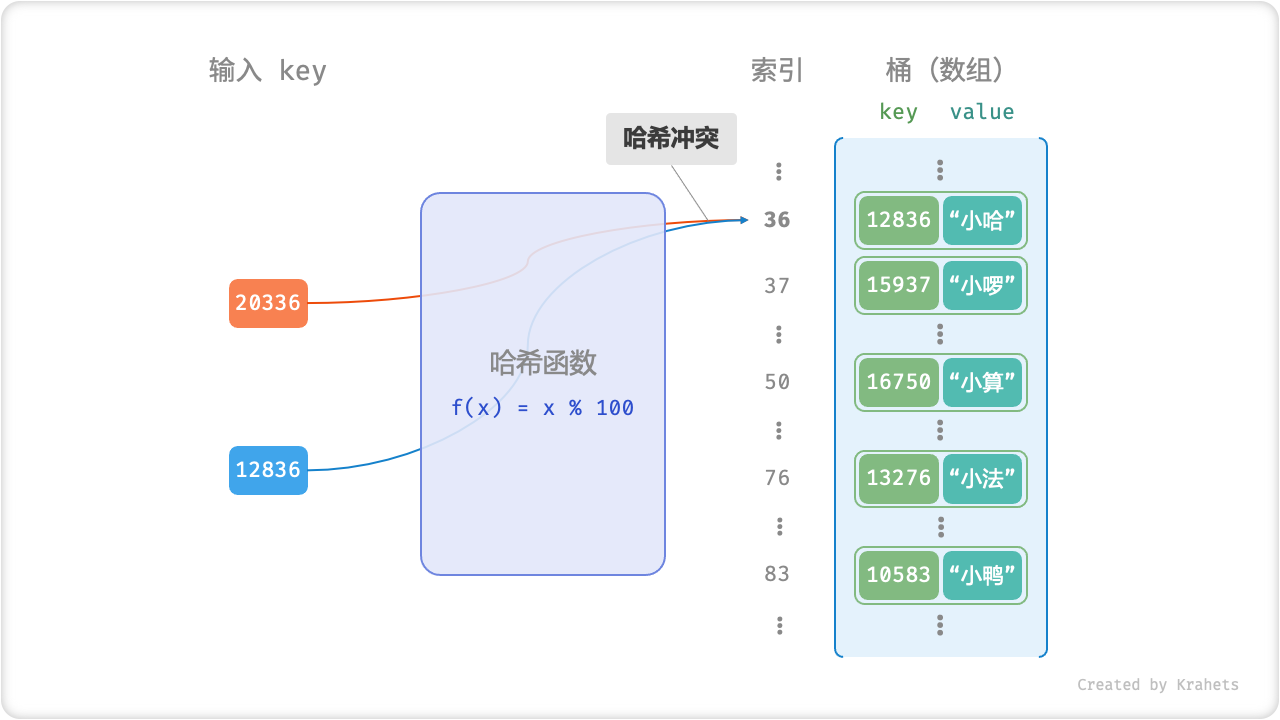
哈希冲突
细心的同学可能会发现,哈希函数 f(x) = x \% 100 会在某些情况下失效。具体地,当输入的 Key 后两位相同时,哈希函数的计算结果也相同,指向同一个 Value 。例如,分别查询两个学号 12836 和 20336 ,则有
f(12836) = f(20336) = 36
导致两个学号指向了同一个姓名,这明显是不对的。我们将这种现象称为「哈希冲突 Hash Collision」,其会严重影响查询的正确性,我们将如何避免哈希冲突的问题留在下章讨论。
Fig. 哈希冲突
综上所述,一个优秀的「哈希函数」应该具备以下特性:
- 尽量少地发生哈希冲突;
- 时间复杂度
O(1),计算尽可能高效; - 空间使用率高,即 “键值对占用空间 / 哈希表总占用空间” 尽可能大;