You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
2.6 KiB
2.6 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
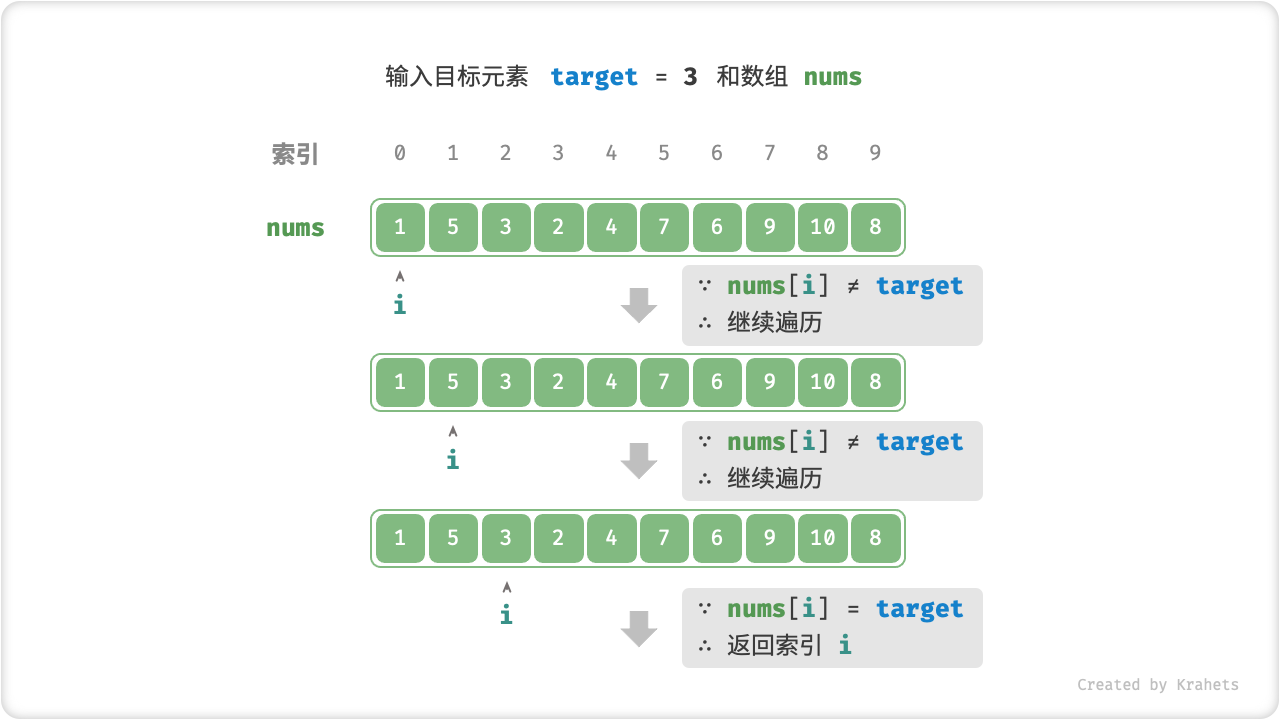
线性查找
「线性查找 Linear Search」是一种最基础的查找方法,其从数据结构的一端开始,依次访问每个元素,直到另一端后停止。
算法实现
线性查找实质上就是遍历数据结构 + 判断条件。比如,我们想要在数组 nums 中查找目标元素 target 的对应索引,那么可以在数组中进行线性查找。
=== "Java"
```java title="linear_search.java"
/* 线性查找(数组) */
int linearSearch(int[] nums, int target) {
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 找到目标元素,返回其索引
if (nums[i] == target)
return i;
}
// 未找到目标元素,返回 -1
return -1;
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="linear_search.cpp"
/* 线性查找(数组) */
int linearSearch(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 找到目标元素,返回其索引
if (nums[i] == target)
return i;
}
// 未找到目标元素,返回 -1
return -1;
}
```
再比如,我们想要在给定一个目标结点值 target ,返回此结点对象,也可以在链表中进行线性查找。
=== "Java"
```java title="linear_search.java"
/* 线性查找(链表) */
ListNode linearSearch(ListNode head, int target) {
// 遍历链表
while (head != null) {
// 找到目标结点,返回之
if (head.val == target)
return head;
head = head.next;
}
// 未找到目标结点,返回 null
return null;
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="linear_search.cpp"
/* 线性查找(链表) */
ListNode* linearSearch(ListNode* head, int target) {
// 遍历链表
while (head != nullptr) {
// 找到目标结点,返回之
if (head->val == target)
return head;
head = head->next;
}
// 未找到目标结点,返回 nullptr
return nullptr;
}
```
复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(n) : 其中 n 为数组或链表长度。
空间复杂度 O(1) : 无需使用额外空间。
优缺点
线性查找的通用性极佳。 由于线性查找是依次访问元素的,即没有跳跃访问元素,因此数组或链表皆适用。
线性查找的时间复杂度太高。 在数据量 n 很大时,查找效率很低。